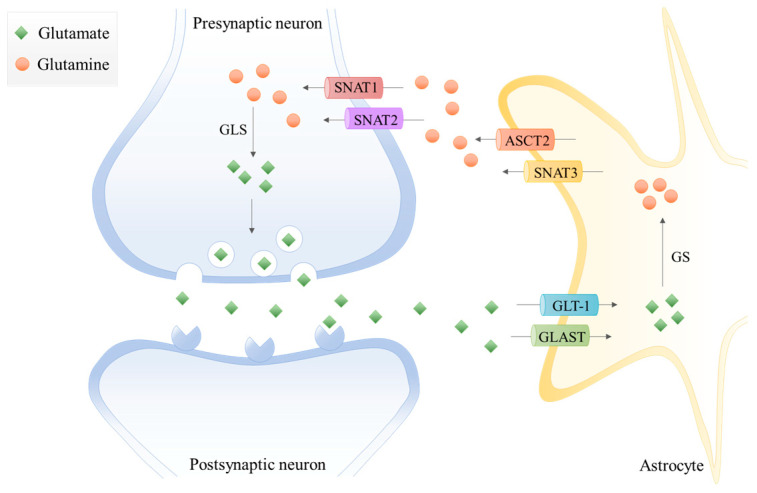
Figure 1.
The glutamate-glutamine cycle in a glutamatergic synapse. The released neurotransmitter glutamate is imported by astrocytes through the glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1) and glutamate aspartate transporter (GLAST). Then, glutamine synthetase (GS) catalyzes the glutamate amidation reaction, generating glutamine using free ammonia. The glutamine is then released from astrocytes via system A amino acid transporter 3 (SNAT3) and alanine/serine/cysteine-preferring transporter (ASCT2) and imported by presynaptic neurons through system A amino acid transporters 1 and 2 (SNAT1 and SNAT2). The glutamine is hydrolyzed to glutamate by glutaminase (GLS), which is packed into synaptic vesicles being sent to the synaptic cleft during neurotransmission. Finally, glutamate is imported again by the astrocytes.