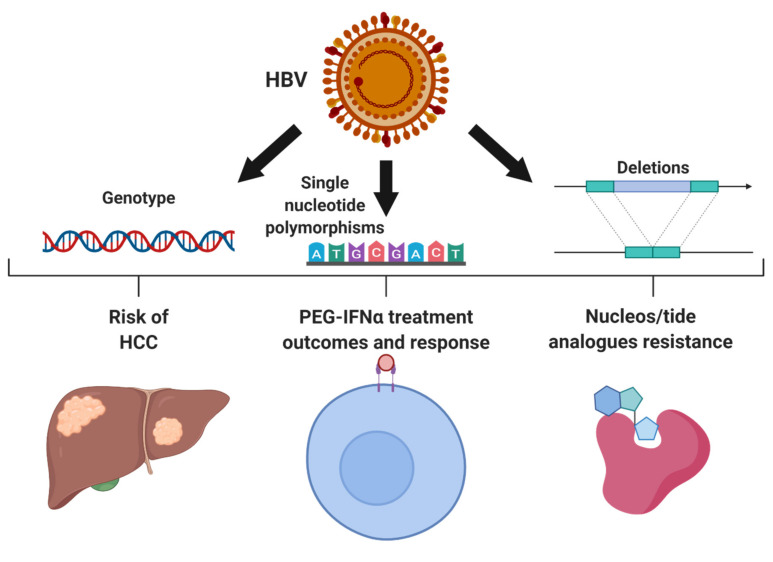
Figure 2.
Impacts of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) genetic variants including genotype, single nucleotide polymorphisms, and deletions of genetic regions. Certain genotypes of HBV are recognized to have higher risks of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and better outcomes to anti-HBV therapeutics such as pegylated-interferon alpha (PEG-IFNα). Similarly, viral genetic polymorphisms particularly in the HBV X/basal core promoter/precore region and the surface region influence HCC risks, PEG-IFNα therapy and viral resistance to nucleos/tide analogues (NA). Figure constructed using Biorender.com.