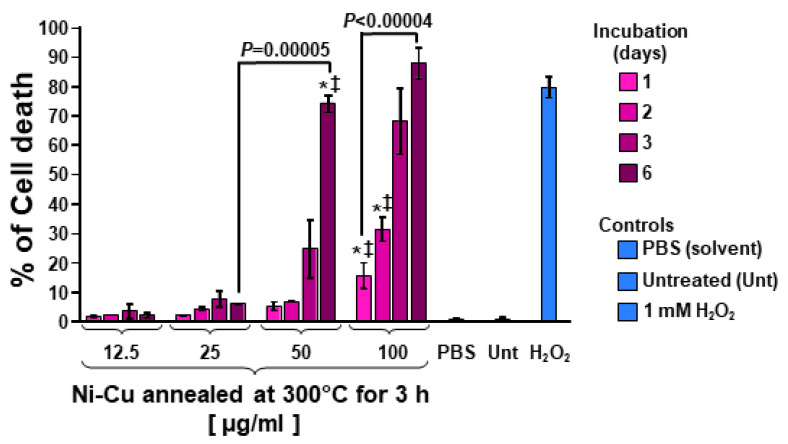
Figure 5.
Ni-Cu magnetic nanoparticles inflict cytotoxicity on human breast MDA-MB231 cells in a dose-dependent manner. These nanoparticles displayed a size of 53 nm and were annealed at 300 °C for 3 h. Cells were incubated for 1, 2, 3, and 6 days with a nanoparticle concentration gradient (in μg/mL). Cellular cytotoxicity (y-axis) was quantified by using the differential nuclear staining assay (DNS: Hoechst and propidium iodide (PI)) and a bioimager system. PBS-treated (1% v/v) cells were used as a solvent control. Untreated (Unt) cells were included as a negative control. In contrast, cells exposed for 24 h to 1 mM of H2O2 were incorporated as a positive control for cytotoxicity. Data acquisition and analyses were accomplished via IN Cell Analyzer Workstation 3.2 software (GE Healthcare). When comparing an experimental sample with PBS-treated (*) or untreated cells (‡), the p-values were both <0.05.