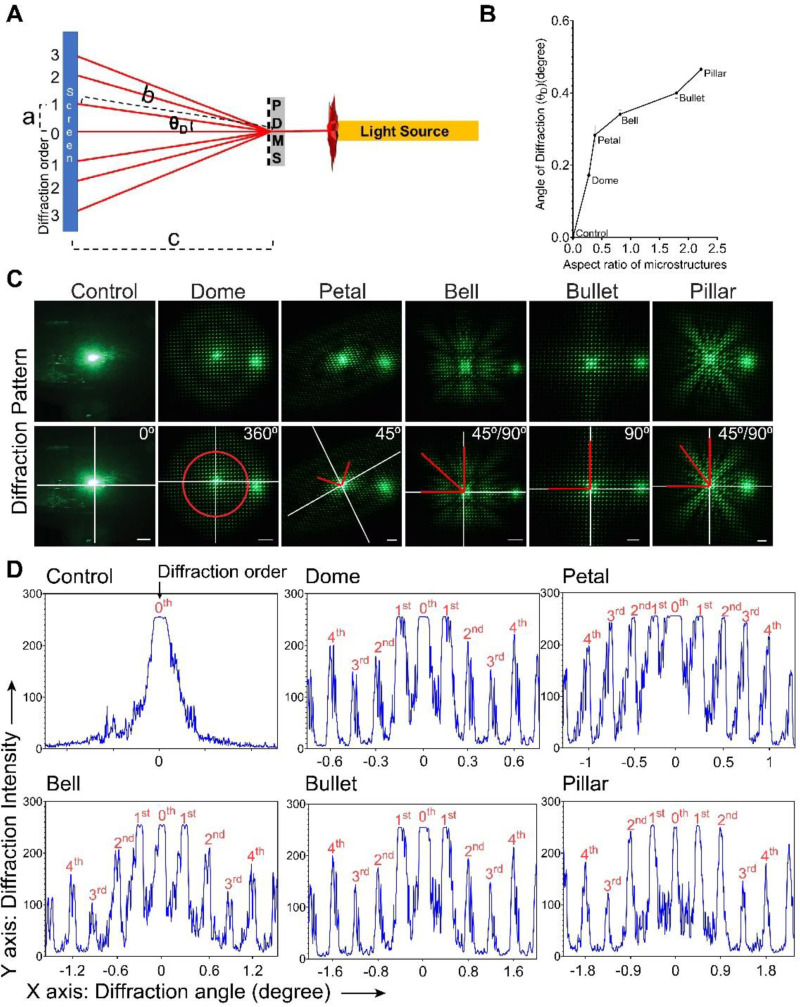
Figure 5.
Characterization of optical diffraction of a monochromatic wavelength passing through the MSAs. (A) Schematic of the optical arrangement to determine diffraction angle. “a” is the distance between 0th (un-diffracted light) and 1st (diffracted light) order of diffractions. “c” is the distance between the MSA and the screen. “b” was calculated based on a and c values. Using these values, the 1st order angle of diffraction, θD, was calculated as the angle between the un-diffracted and first-order diffracted light. (B) The angle of diffraction, θD, as a function of the MSA aspect ratio. (C) Top row: Diffraction pattern of the monochromatic light through the DEL-MSA grating. Note that the brightest intensity observed on the right side in the diffraction images was an artifact that occurred during image capturing and was not considered for any calculations or conclusions. Bottom row: The angle of diffraction along the brightest intensity path was notated: white lines indicate the x- and y-axis passing through the 0th order of diffraction, which was the reference to calculate the diffraction pattern angle (indicated by the red lines). The numbers indicate the brightest light diffraction angle. (D) Intensity profile of the diffraction pattern (up to 4th order) as a function of diffraction angle. Error bars: (B) STDEV. Scale bar: (C) 3 cm.