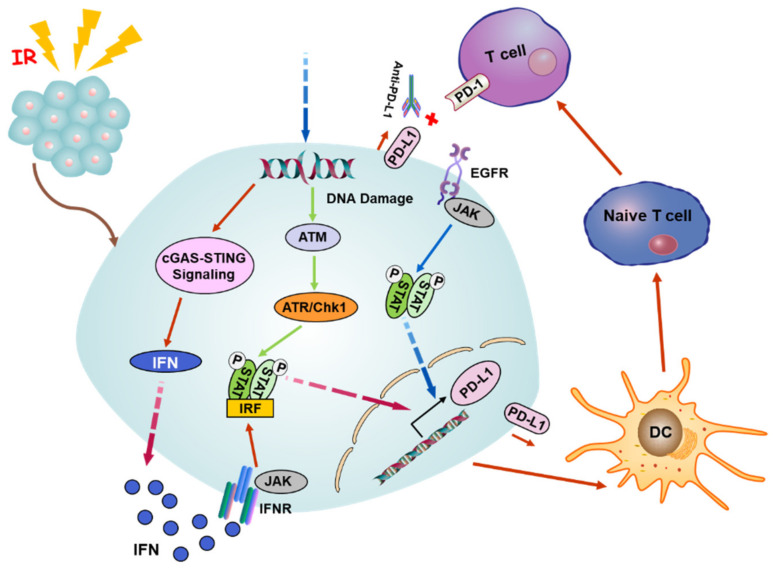
Figure 2.
A potential mechanism of radiation-induced abscopal effect. Radiation triggers the release of nuclear DNA into the cytoplasm, and cGAS can recognize the damaged DNA and activate the cGAS-STING pathway to induce the secretion of IFN-I that can bind to the cell surface receptor INFR to activate the axis of Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription/interferon regulatory factor (JAK/STAT/IRF). Meanwhile, the DNA damage also stimulates the ATM/ATR/Chk1 signaling followed by the STAT-IRF pathway. The phosphorylated STAT/IRF complex can be translocated to the nucleus and targets the promoter of PD-L1 to boost the expression of PD-L1. Alternatively, the expression of PD-L1 is upregulated by EGFR receptor activation through JAK/STAT signaling upon radiation. The combination of anti-PD-L1 and PD-L1 breaks the connection between PD-L1 and PD-1, making tumor cells unable to escape from the immune supervision of T cells. Abbreviations: cGAS, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; IFN-I, type I interferon; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor.