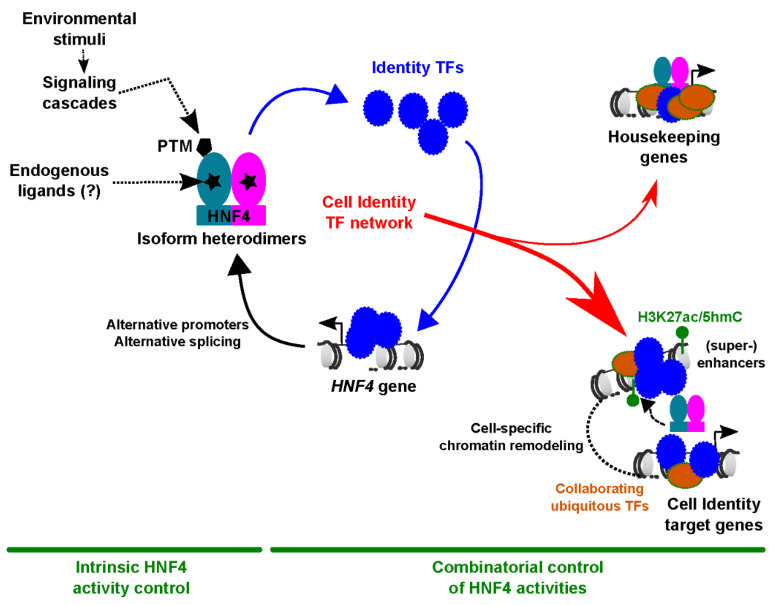
Figure 1.
Mechanisms involved in the control of cell identity by HNF4. Intrinsic control of HNF4 activities through isoform heterodimers, post-translational modifications (PTMs), and potential ligands add up to the modulation of its functions through involvement in cell-specific transcription factor (TF) networks. Combinatorial control of cell identity by HNF4 and additional cell identity by TFs consist of 2 interdependent layers where these TFs modulate each other’s expression and coordinately regulate common (non-TF) cell identity target genes.