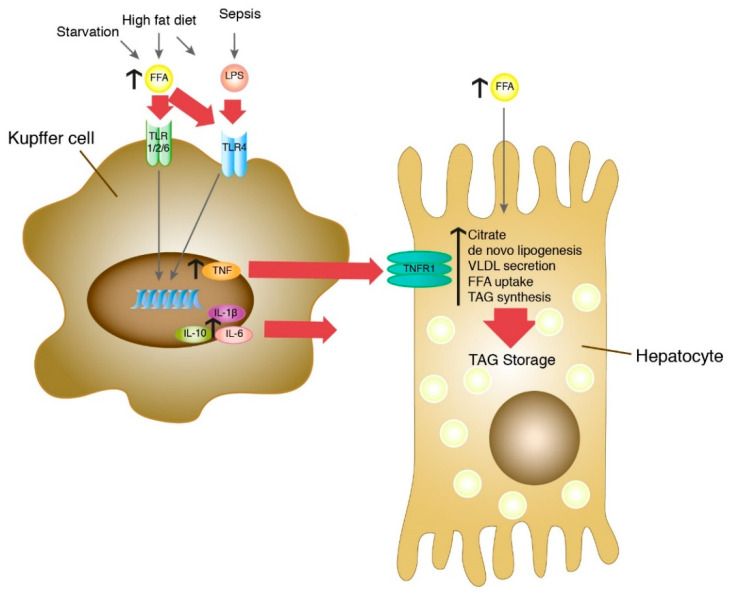
Figure 8.
The role of Kupffer cells as hepatic sensory cells in the development of steatosis in hepatocytes. Increased FFA can be caused by lipolysis in adipose tissue during starvation or by excess nutritional intake in high-fat diet. Elevated LPS levels can be caused by high-fat diet or sepsis. Both FFA and LPS bind to Toll-like receptors on the surface of Kupffer cells and lead to increased secretion of IL-1β, IL-10 und IL-6 and TNF. Secreted TNF binds to the TNFR1 receptor on hepatocytes and leads to increased citrate levels, de novo lipogenesis, FFA uptake and TAG synthesis and to a reduced VLDL secretion. As a result, this leads to an increased TAG storage and formation of steatosis in hepatocytes. In this model, the Kupffer cell is the primary sensor for both FFA overload and LPS, integrates these signals and utilizes TNF to transmit the information to the hepatocyte, which reacts by alteration of lipid metabolism.