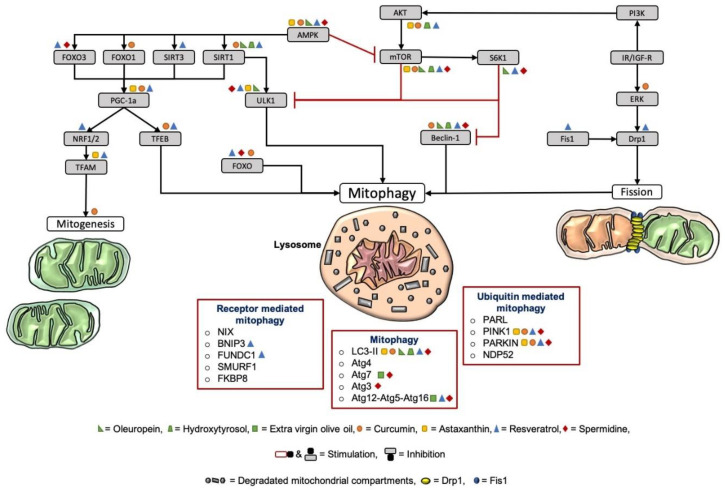
Figure 4.
Target points of the dietary compounds on mitochondrial dynamics and mitogenesis, with a particular focus on mitophagy. AMPK is one of the central upstream regulators of mitophagy and mitogenesis. Through oxidative-stress, induced mtDNA mutation activates the AMPK pathway and further inhibits the mTOR [46]. AMPK, in turn, stimulates mitophagy via ULK1 and mitogenesis via the PGC-1 α pathway. The main upstream mediators of PGC-1 α are FOXO1/3 and SIRT1/3. PGC-1 α, in turn, activates mitophagy via NRF1/2 and TFAM. Paradoxically, the mitogenesis promoter PGC-1 α also interferes with mitophagy by regulating lysosomal biogenesis via TFEB. Further, AMPK targets FOXO1 and -3. FOXO, in turn, increases the transcription of essential mitophagy mediators and proteins. On the other hand, mTOR blocks mitophagy by inhibiting ULK1 as well as downstream signaling of ribosomal protein S6K1, which, in turn, also suppresses mitophagy by indirectly inhibiting ULK1 and Beclin-1. The upstream modulator of mTOR is the IR/IGF-R, which activates PI3K, followed by activation of AKT, which activates mTOR. ERK, in turn, phosphorylates Drp1 for mitochondrial fragmentation and stimulates mitophagy due to the activation of IR/IGF-R signals. In general, Fis1 is recruiting Drp1 to the OMM to induce mitochondrial fission. In this figure, the target points of the most prominent compounds of both the Mediterranean and the Asian/Okinawan diets are displayed. Hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein from olive oil, curcumin, astaxanthin, resveratrol, and spermidine were all found to stimulate mitochondrial dynamics, mitogenesis, and, especially, mitophagy. Abbreviation: AMPK = AMP-activated protein kinase; mtDNA = mitochondrial DNA; mTOR = mammalian target of rapamycin; ULK1 = unc-51-like kinase 1; PGC-1 α = peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; FOXO1/3 = forkhead transcription factor 1/3; SIRT1/3 = silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 1/3; NRF1/2 = nuclear respiratory factor 1 and 2; TFAM = mitochondrial transcription factor A; TFEB = transcription factor EB; S6K1 = S6 kinase beta-1; IR/IGF-R = insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor; PI3K = phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT = protein kinase B; ERK = extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Drp1 = dynamin-related protein 1; Fis1 = fission protein 1; OMM = outer mitochondrial membrane.