Figure 11.
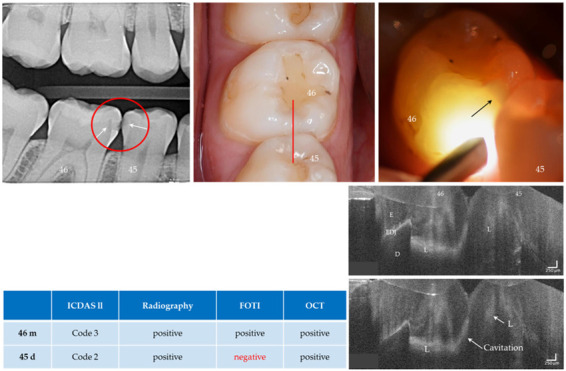
Teeth 46 (m) and 45 (d). Both surfaces showed visual and radiographic caries lesions (L, arrows) and dentin involvement was visible on tooth 46. The FOTI showed no signal on tooth 45 distally (arrow indicates the lesion of tooth 46), while a weak signal was visible on OCT. In the OCT images of tooth 46, dentin involvement is clearly visible and cavitation can be assumed due to the diagonal signal line (see Fig. 5b) and the anatomy of the tooth surface. Verification: Both the early carious lesion on tooth 45 and the cavitated lesion on tooth 46 could be confirmed later during the restoration of tooth 46. Enamel (E), dentin (D), enamel-dentin junction (EDJ). The vertical scales are related to refractive index n = 1.5.
