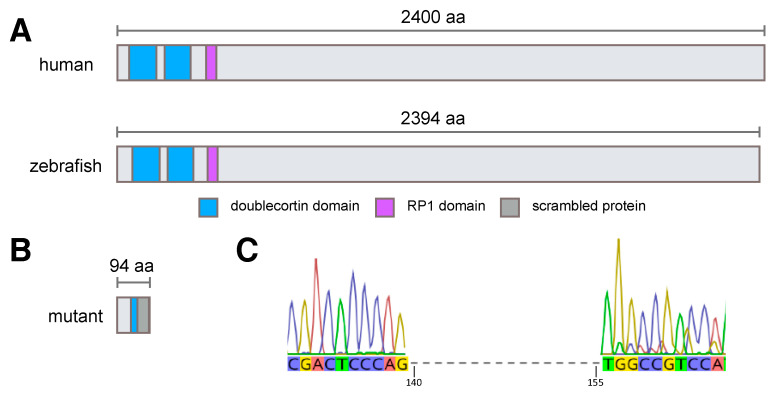
Figure 1.
Human and zebrafish RP1L1 proteins have conserved domains, which are predicted to be eliminated in rp1l1 mutant zebrafish. (A) Cartoon of human and wild-type zebrafish proteins. Human and zebrafish RP1L1 have conserved domains and are similar sizes, with human RP1L1 protein being 2400 amino acids (aa) and zebrafish Rp1l1 protein being 2394 amino acids in length. (B) The mutation in zebrafish rp1l1 is predicted to result in a severely truncated, nonfunctional Rp1l1 protein. The mutation occurs in the first doublecortin domain of Rp1l1 after amino acid 52, resulting in significant loss of more than half of the doublecortin domain, which is followed by an abnormal protein extension and termination at 94 amino acids in length. (C) The CRISPR/Cas9-generated 16 bp deletion in zebrafish rp1l1 occurs after nucleotide 139.