Figure 2.
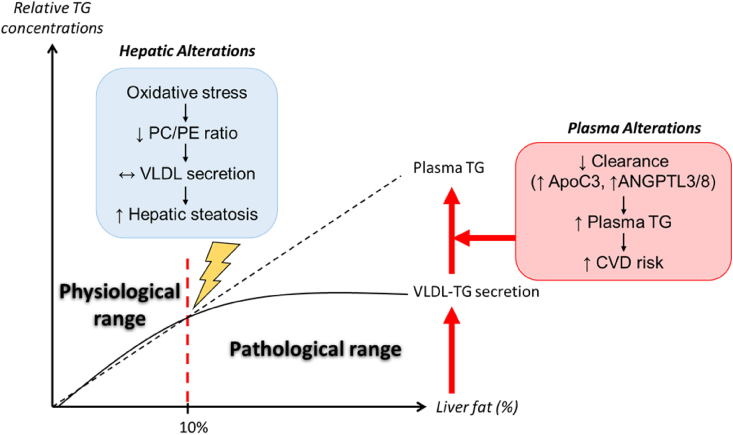
The dynamic balance between hepatic VLDL-TG secretion and plasma clearance determines the association between NAFLD and plasma triglycerides. When intrahepatic triglycerides reach of a ∼10% level, oxidative stress increases, leading to decreased PC availability, preventing further increases in hepatic VLDL-TG secretion, thereby favoring hepatic steatosis. In parallel, circulating inhibitors of lipoprotein lipase such as ApoC3 and ANGPTL3/8 increase due to the presence of insulin resistance and exacerbate plasma hypertriglyceridemia by reducing intravascular TG hydrolysis. The dynamic balance between these factors explains the positive correlation between plasma hypertriglyceridemia and hepatic steatosis.