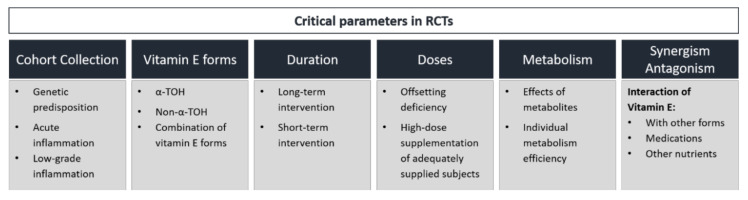
Figure 4.
Critical parameters in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating beneficial effects of vitamin E supplementation on CVD. Vitamin E is the most prominent lipid-soluble antioxidant additionally possessing anti-inflammatory capacity. However, in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) supplementation of vitamin E has revealed controversial effects on the risk of cardiovascular events. The reasons for these findings are diverse. The most common reasons discussed are: cohort selection, the form of vitamin E used for treatment and the treatment durations and doses of vitamin E, the relevance of hepatically formed metabolites, and the synergistic or antagonistic effects of different vitamin E forms on each other or on nutritional factors and medications.