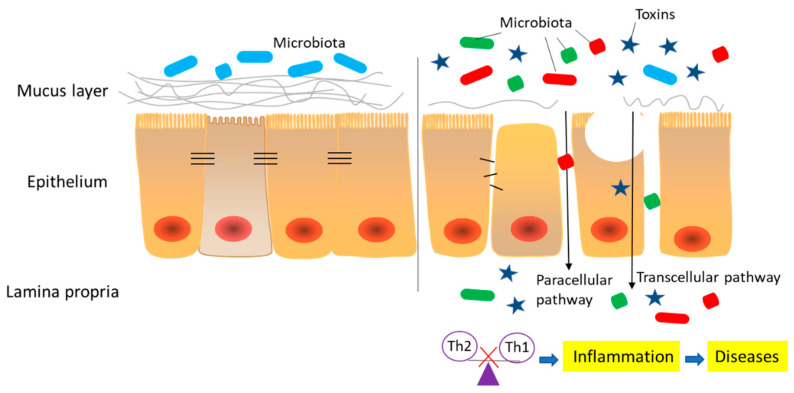
Figure 2.
Summary of the negative effects induced by mycotoxins on intestinal barrier. Relevant aspects include (i) increased permeability (paracellular and transcellular transport), which is induced by disrupted epithelial cells and tight junctions, and (ii) the thinned mucus layer. The compromised intestinal barrier results in the penetration of xenobiotics of different molecular weights and bacterial translocation, ultimately contributing to an imbalance of inflammatory responses and the activation of local and systemic immunity, causing the occurrence of inflammatory-related diseases.