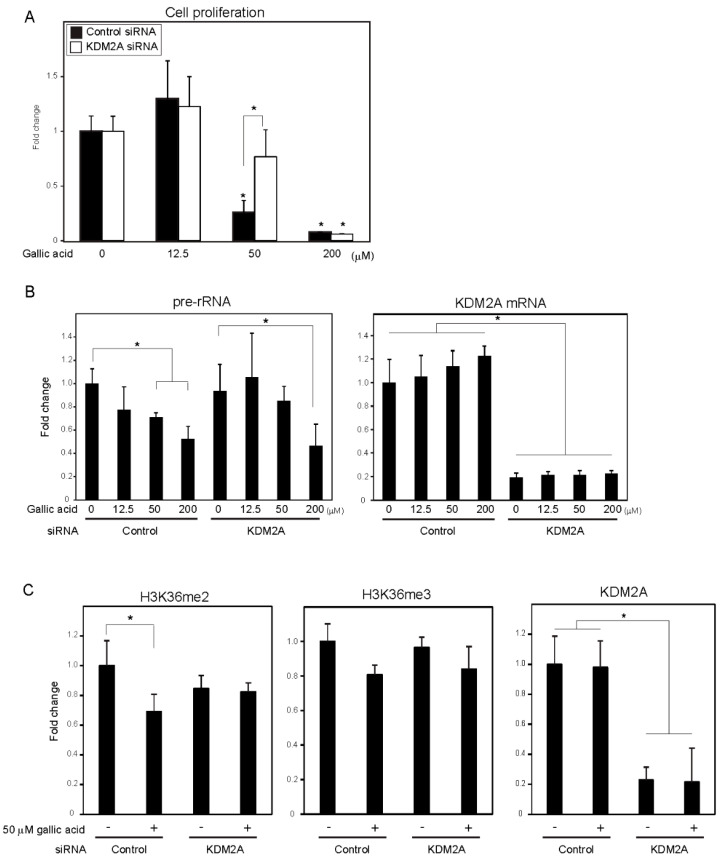
Figure 1.
Gallic acid induced KDM2A-dependent reductions of cell proliferation, rRNA transcription, and H3K36me2 in rDNA promoter in MCF-7 cells. (A) Gallic acid decreased proliferation of MCF-7 cells through KDM2A. MCF-7 cells transfected with control siRNA or siRNA for KDM2A were cultured with gallic acid as indicated concentrations for 2 days. Cell numbers were measured by CyQUANT® Direct Cell Proliferation Assay detecting DNA content. (B) The treatment with 50 μM gallic acid reduces rRNA transcription through KDM2A. MCF-7 cells transfected with control siRNA or siRNA for KDM2A were treated with gallic acid at indicated concentrations for 4 h. Total RNAs were isolated and analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) to detect rRNA transcription (pre-rRNA) (left panel) and KDM2A mRNA (right panel). The ratios of the values for cells treated with various conditions to those for cells treated with control siRNA without gallic acid are shown. (C) KDM2A-dependent reduction of H3K36me2 marks in rDNA promoter by treatment with 50 μM gallic acid. MCF-7 cells transfected with control siRNA or siRNA for KDM2A were treated with 50 μM gallic acid for 4 h. The levels of H3K36me2, H3K36me3, and KDM2A in the rDNA promoter were analyzed by ChIP assay. The results are expressed as fold changes of the values under various conditions to those in cells cultured with control siRNA without gallic acid treatment. All experiments were performed more than three times, and the mean values with standard deviations are indicated. * p < 0.05.