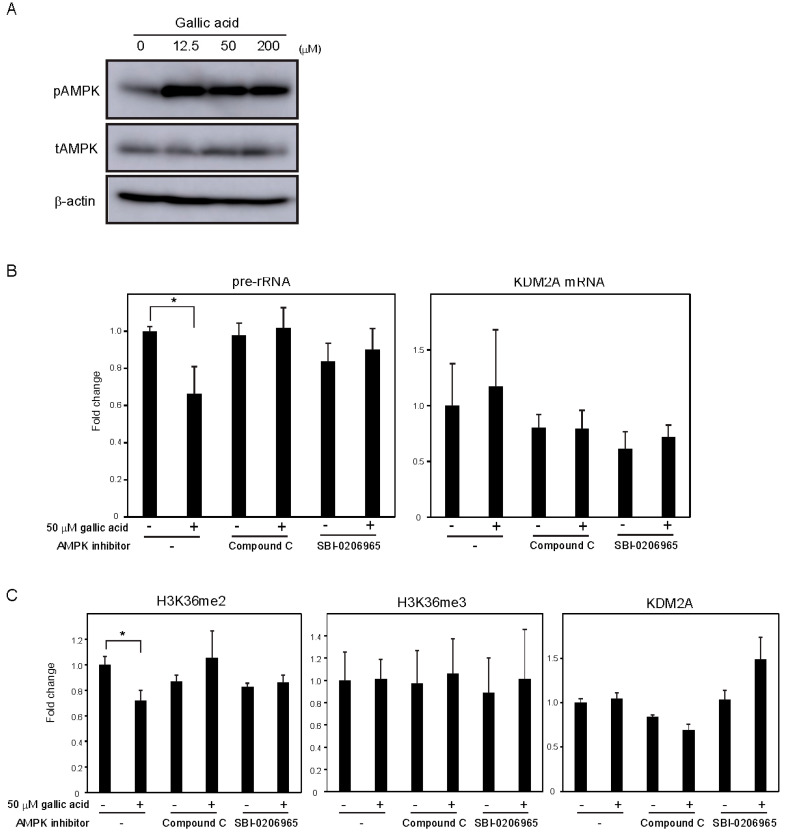
Figure 3.
AMPK activation is required for the KDM2A-mediated repression of rRNA transcription by gallic acid in MCF-7 cells. (A) Activation of AMPK by gallic acid in MCF-7 cells. MCF-7 cells were treated with gallic acid as indicated concentrations for 4 h. Cells were lysed and analyzed for the levels of phosphorylated-AMPKα (Thr172) (pAMPK), total AMPKα (tAMPK), and β-actin by immunoblotting. (B) Requirement of AMPK activity for the reduction of rRNA transcription by gallic acid. MCF-7 cells treated with or without 50 μM gallic acid in the presence or absence of AMPK inhibitor, 10 μM compound C or 5 μM SBI-0206965, for 4 h. Total RNAs were isolated and analyzed by qRT-PCR to detect pre-rRNA (left panel) and KDM2A mRNA (right panel). The ratios of the values for cells treated with various conditions to those for cells treated without gallic acid and AMPK inhibitors are shown. The experiments were performed three times (n = 3), and the mean values with standard deviations are indicated. * p < 0.05. (C) Requirement of AMPK activity for the reduction of H3K36me2 mark in the rDNA promoter by gallic acid. MCF-7 cells treated with or without 50 μM gallic acid in the presence of 10 μM compound C or 5 μM SBI-0206965 for 4 h. The levels of H3K36me2, H3K36me3, and KDM2A in the rDNA promoter were analyzed by ChIP assay. The results are expressed as fold changes to the values in various conditions to those without gallic acid and AMPK inhibitors. The experiments were performed three times (n = 3), and the mean values with standard deviations are indicated. * p < 0.05.