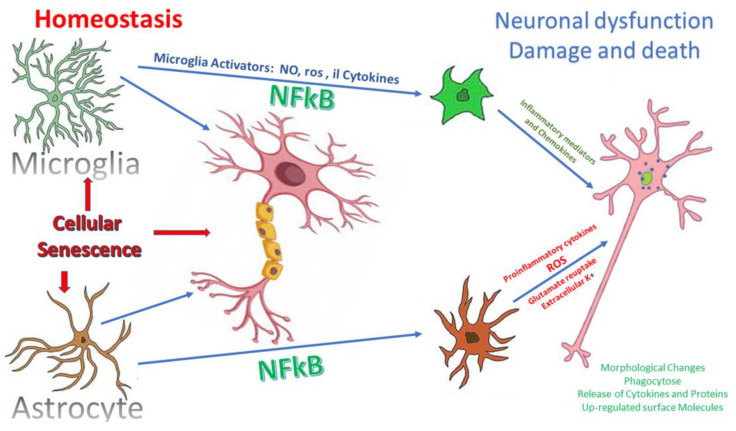
Figure 3.
Under physiological conditions, microglia maintain the synapses and their plasticity but signaling pathways, such as NF-κB, can be activated in various ways. The activated microglia and reactive astrocytes produce ROS and neurotoxic molecules which can lead to neuronal death. In addition, the senescence of microglia and astrocytes causes inflammation and a loss of trophic support. The senescence of the oligodendrocytes reduces the myelin and influences the nerve transmission, while the senescence of the endothelial cells influences the barrier functionality. Reactive astrogliosis with up-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine production, excitotoxicity of glutamate and hyperexcitability of neurons may also occur.