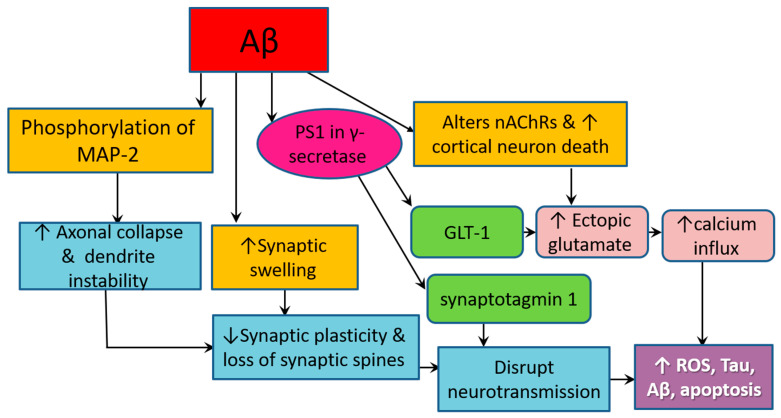
Figure 3.
Schematic illustration of the mechanism underlying synaptic destruction by beta-amyloid peptide (Aβ). Abbreviations: ↑ denotes increase, ↓ denotes decrease, Aβ: beta-amyloid protein fragments, MAP-2: microtubule-associated protein 2, PS1: presenilin 1, nAChRs: nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, GLT-1: glutamate transporter 1, ROS: reactive oxygen species. Aβ pathology contributes to synaptic destruction, which promotes neuronal apoptosis through various mechanisms.