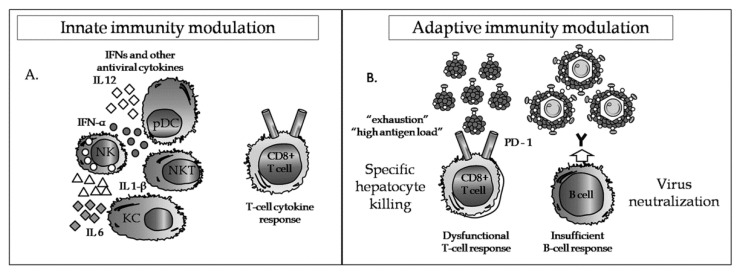
Figure 2.
(A) HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBx can interfere with the innate immune response and in particular components of signal transduction pathways or other processes which, in turn, can disregulate IFN and antiviral cytokine production by effector cells such as natural killer (NK), NK T cells (NKT), kuppfer cells (KC) and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC). Such events may inhibit CD4+ and CD8+ T cells; Interferons (INFs (B) The adaptive immune response relies on the production of virus neutralizing antibodies and cytotoxic T cells for lysis of infected hepatocytes. However, chronic HBV infection is characterized by the loss or functional exhaustion of HBV-specific CD8+ T cells due to high levels of HBs antigenaemia and failure to neutralize circulating virions as a result of an insufficient B-cell response. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1).