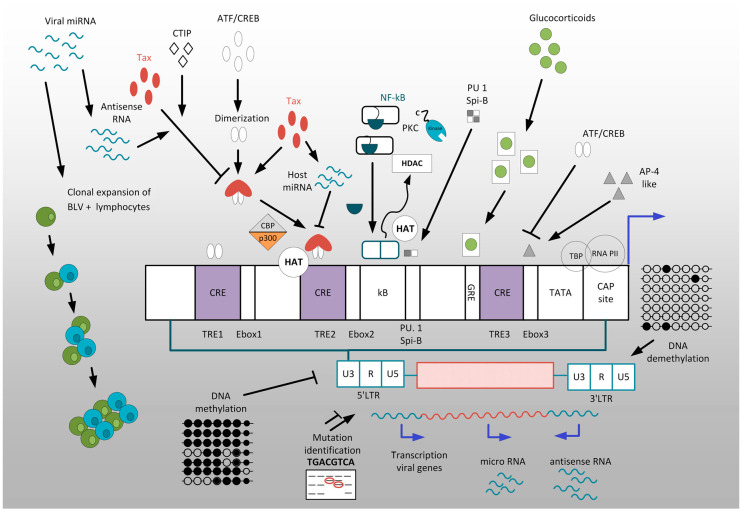
Figure 2.
A schematic diagram of regulation of expression in BLV. The scheme illustrates the interactions that induce 5′LTR transcription: TRE element and the Tax/ATF/CREB and CBP/p300 complexes; NF-kB, PKC, and HAT; glucocorticoid receptor (GR), glucocorticoids and glucocorticoid response element (GRE); demethylation within 3′-LTR; some mutations within regulatory elements of the LTR; and the interaction that repress 5′LTR transcription: antisense RNA and Tax; CTIP and Tax; NF-kB and HDAC; AP-4 like protein ATF/CREB and E box; methylation within 5′-LTR; some mutations within the LTR. Black sharp arrows indicate an induction of 5′LTR transcription, black blunt arrows indicate repression of 5′LTR transcription. Clonal expansion of BLV+ lymphocytes is another mode of viral propagation. Transactivation of transcription at the viral LTR is a critical role of Tax in BLV infected cells as this ultimately leads to the expression of all viral genes. The LTR is divided into the U3, R and U5 regions. The U3 region is of significant importance in Tax-mediated transcription and thus is highlighted in the expanded box. This region contains three TRE-1,2, 3 and CRE regions; Ebox1,2,3; κB; PU.1/Spi-B region; GRE; TATA box and CAP site.