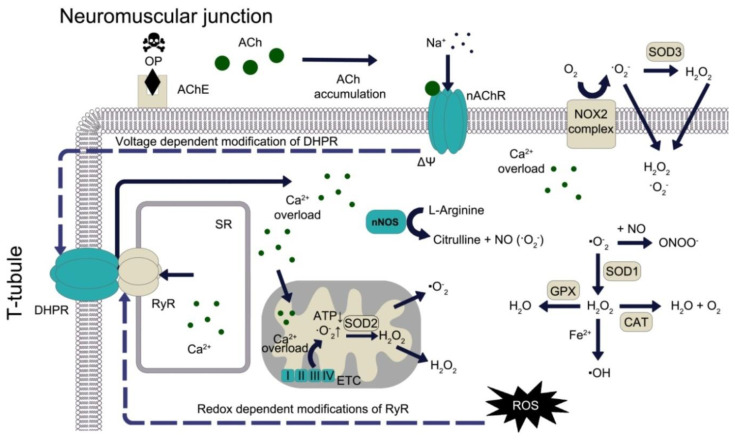
Figure 1.
Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the mechanism of toxic effects of organophosphates on skeletal muscle. OP—organophosphate; ACh—acetylcholine; AChE—acetylcholinesterase; nAChR—nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; nNOS—neuronal nitric oxide synthases; ATP—adenosine triphosphate; SOD—superoxide dismutase; ETC—electron transport chain in mitochondria; DHPR—Dihydropyridine receptor; RyR—Ryanodine receptor; SR—Sarcoplasmic reticulum; NOX—NADPH oxidase; GPx—Glutathione peroxidase; CAT—Catalase.