Figure 1.
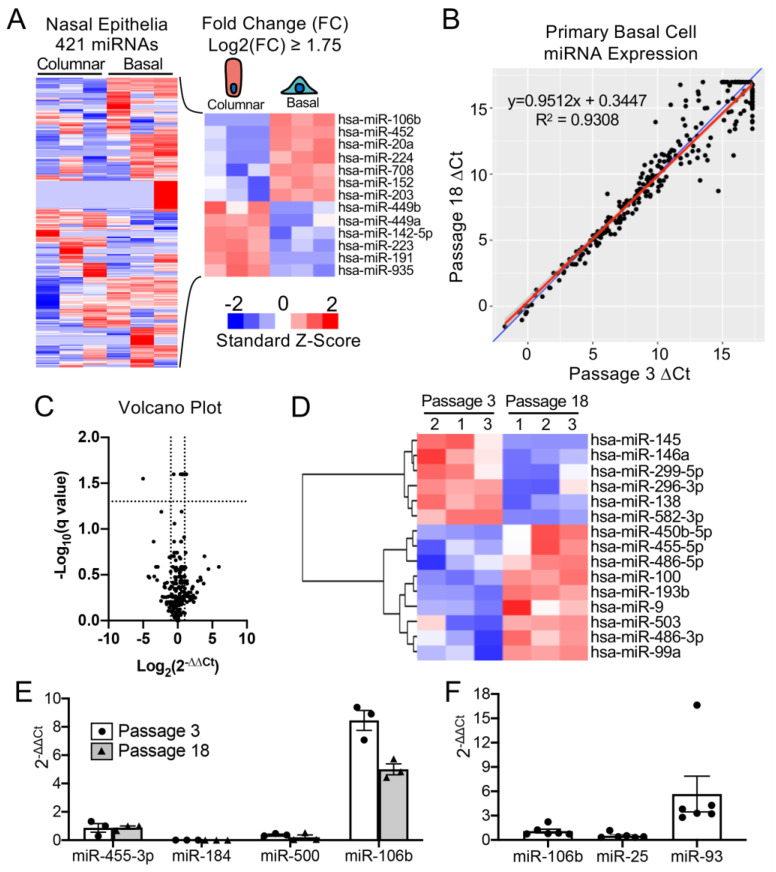
mMiR-106b is stably expressed at high levels in proliferating human basal cells. (A) Published data of miRNAs detected by high throughput sequence profiling of nasal basal cells and columnar cells (Accession: GSE22145) were used to generate a heatmap of 421 expressed miRNAs (left) and 13 miRNAs with a Log2 fold difference greater than 1.75 or less than −1.75 (right). (B) Correlation of miRNA expression in basal cells at Passage 3 and Passage 18 detected by qPCR array with the blue line represents a theoretical perfect correlation (x = y), and the red line represents linear regression model. (C) Volcano plot of miRNA array data indicating genes that were differentially expressed between passages 3 and 18. (D) Heatmap of miRNA array data with unsupervised hierarchical clustering of 15 miRNAs (of 252 detected) with an absolute fold change ≥ 2 and an unadjusted p value of ≤0.05. (E) Relative quantification of candidate basal cell-specific miRNAs, miR-184, miR-500, and miR-106b compared to a known basal cell-specific miR-455-3p. Freshly isolated primary human tracheobronchial cells were passaged 3 (P3) and 18 (P18) times in SAGM-EA media (N = 3). (F) Relative quantification of miRNAs belonging to miR-106b-25 cluster in passage 3 basal cells (N = 6). Each dot represents one donor.