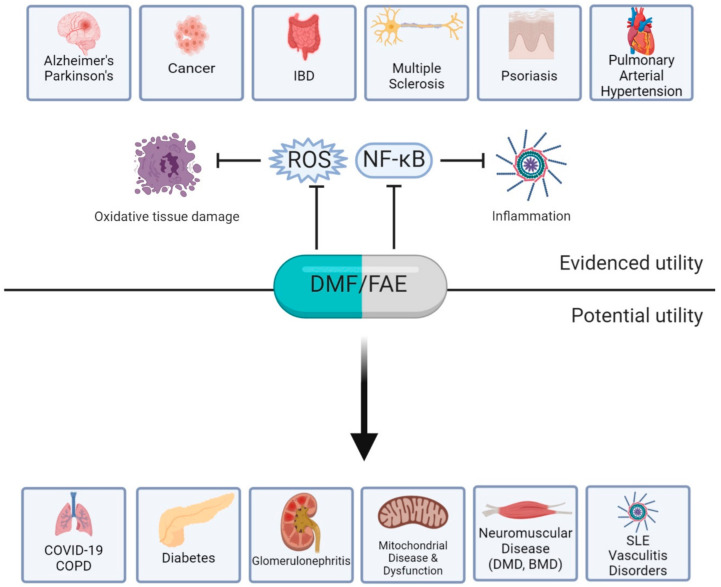
Figure 1.
Approved and evidenced utility of dimethyl fumarate (DMF) and fumaric acid esters (FAE) versus potential utility in other diseases that are underscored by oxidative stress and hyperinflammation. DMF and FAE can exert their effects by enhancing cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory responses. This is proposed to lead to the reduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which in turn prevents oxidative tissue damage. DMF also inhibits nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), which subsequently reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine production and immune cell deviation and ultimately leads to reduced inflammation. BMD: Becker Muscular Dystrophy; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DMD: Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy; IBD: inflammatory bowel disease; SLE: systemic lupus erythematosus. Bar heads = inhibitory effect; Arrow heads = potential beneficial effect. Created with BioRender.com.