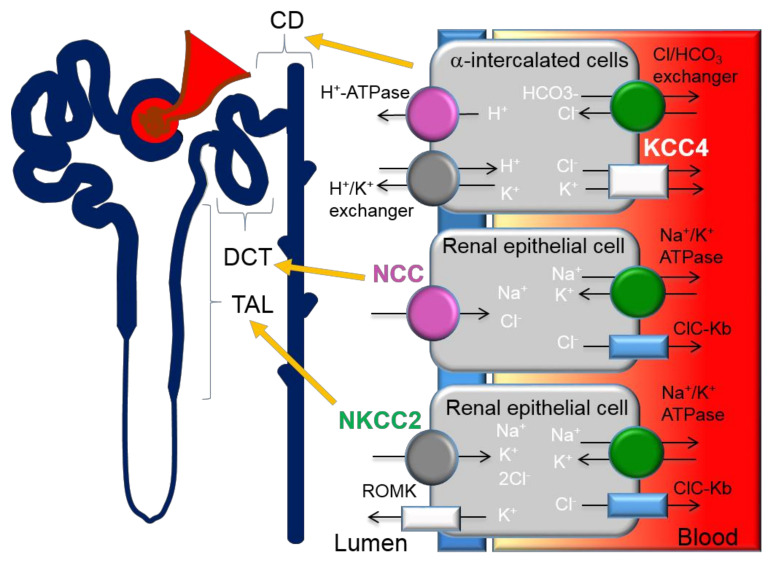
Figure 1.
Expression of cation-chloride-cotransporters in the kidney. Alpha-intercalated cells in the collecting duct (CD) secretes acid via the apical H-ATPase and H+/K+ exchanger and reabsorbs bicarbonate via the basolateral Cl/HCO3 exchanger. Efflux of Cl− through the potassium chloride co-transporter-4 (KCC4) is important to maintain the electrochemical gradient to facilitate the acid secretion activities of the alpha-intercalated cells. Loss of KCC4 leads to renal tubular acidosis, which, if left untreated, could lead to cardiac arrhythmias. Sodium-chloride-cotransporters (NCCs) are exclusively expressed in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT). Gain-of-function mutations in regulatory genes that lead to the over activation of NCC cause Familial Hyperkalemic Hypertension (FHHt). Sodium potassium chloride cotransporters-2 (NKCC2) is expressed in the thick ascending limb (TAL). Loss-of-function mutations of NKCC2 results in the salt-wasting phenotype of type 1 Bartter Syndrome.