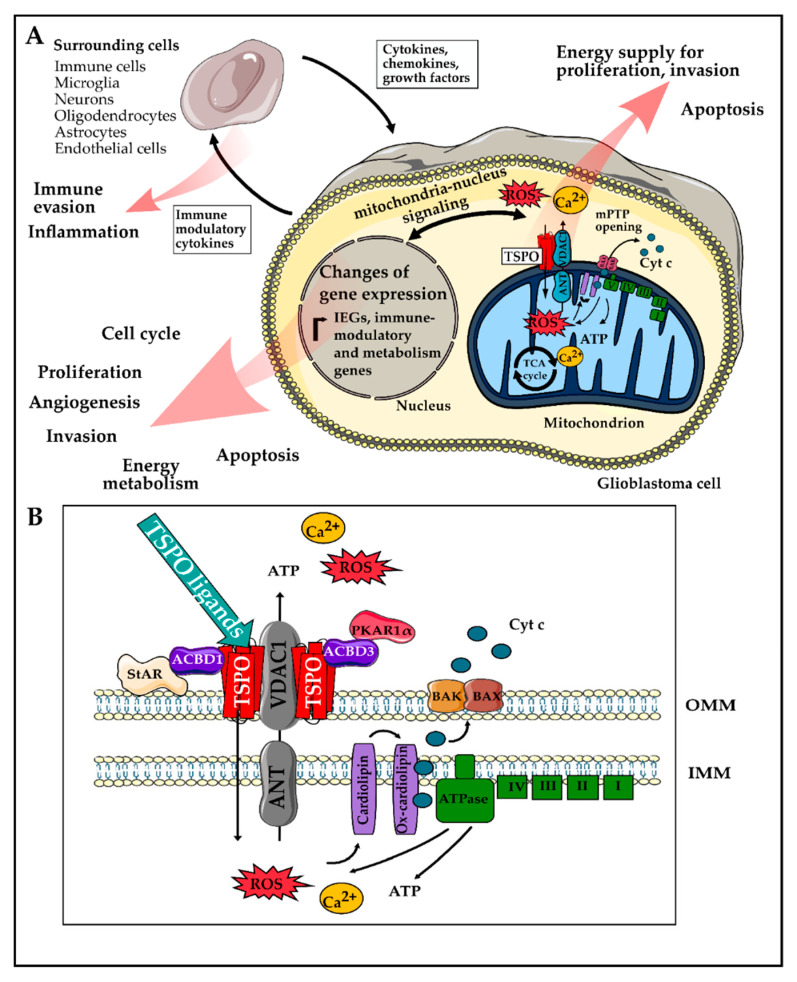
Figure 2.
Overview of the mechanisms of how TSPO could modulate the hallmarks of Glioblastoma (GBM). (A) TSPO, together with other mitochondrial proteins such as voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), adenine nucleotide transporter (ANT), and ATPase can modulate mitochondrial Ca2+ release, ATP production, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. The latter can then lead to the release of cyt c, which triggers the mitochondrial apoptosis cascade and ultimately apoptosis. An increase in ATP production, on the other hand, could provide energy for enhanced proliferation and invasion of GBM cells. The mitochondrial ROS, ATP, and Ca2+ release are also considered as a part of the mitochondria to nucleus signaling, which can modulate the expression of immediate early genes and transcription factors, as well as metabolism-related and immune-modulatory genes [124,127]. Several hallmarks of GBM can be modulated as a functional consequence of these gene expression changes. Furthermore, the immune-modulatory factors and cytokines secreted by the tumor cell can modulate surrounding cells contributing to immune escape and a tumor-promoting microenvironment [182,183]. (B) Close up showing the proposed working mechanism: TSPO is located in the outer mitochondrial membrane and can be found in close proximity to several cytosolic proteins such as StAR, ACBD1, ACBD3, and PKAR1α, which have been described to play a role in steroidogenesis (reviewed by [216]). Furthermore, binding of TSPO ligands to TSPO, in interaction with VDAC1, can modulate ROS and ATP production by modifying the activity of the ATPase [200,201]. An increase in the levels of ROS can result in cardiolipin oxidation and opening of the mPTP, consisting of VDAC1 and ANT [21,75,151]. The opening of the mPTP causes the release of ATP, ROS, and Ca2+ from the mitochondria into the cytosol and the collapse of the ΔΨm. The depolarization then leads to the opening of BAK/BAX channels, allowing the passage of cyt c into the cytosol. Abbreviations: ACBD, acyl-CoA-binding domain protein; cyt c, cytochrome c; IEG, immediate early genes; ROS, reactive oxygen species; mPTP, mitochondrial permeability pore; ΔΨm, mitochondrial membrane potential; PRKAR1α, protein kinase cAMP-dependent type I regulatory subunit alpha; StAR, steroidogenic acute regulatory protein.