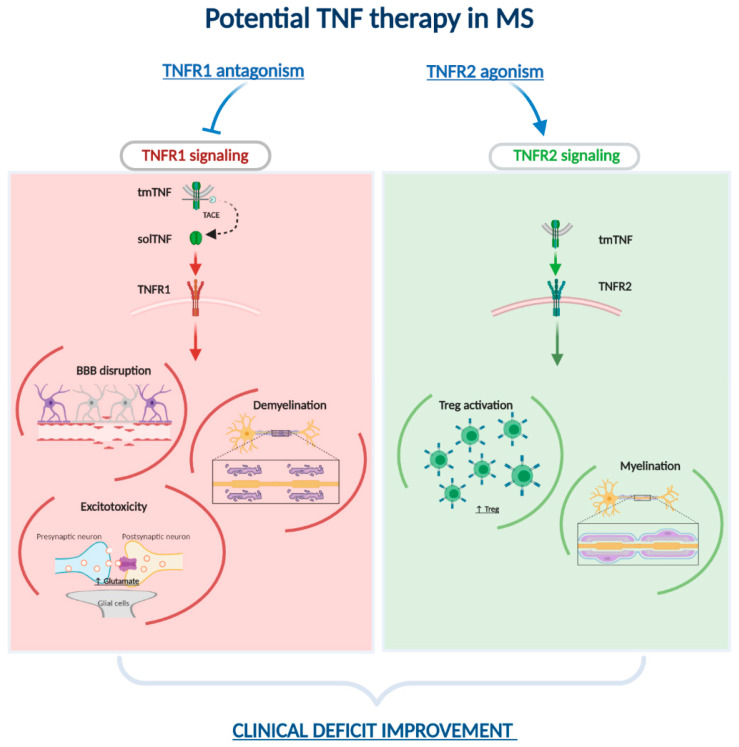
Figure 1.
Potential working model of TNF therapy in MS. TNF exists in two different forms, tmTNF (transmembrane) and solTNF (soluble), this latter synthetized by TACE enzymatic activity and thus released only by TACE expressing cells. solTNF binds preferentially TNF receptor type-1 (TNFR1) while tmTNF recognizes type-2 (TNFR2). TNF and its receptors are involved in many pathological processes of MS. Signaling through TNFR1 is likely responsible for BBB disruption, demyelination and glutamate-excitotoxity, while TNFR2 activation by tmTNF is supposed to promote myelination and Treg expansion and activation. The combination of molecules selectively modulating TNFRs signaling through TNFR1 antagonism and TNFR2 agonism is proposed as a putative novel approach for MS treatment. BBB, blood–brain barrier; Tregs, regulatory T cells; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TACE, TNF converting enzyme.