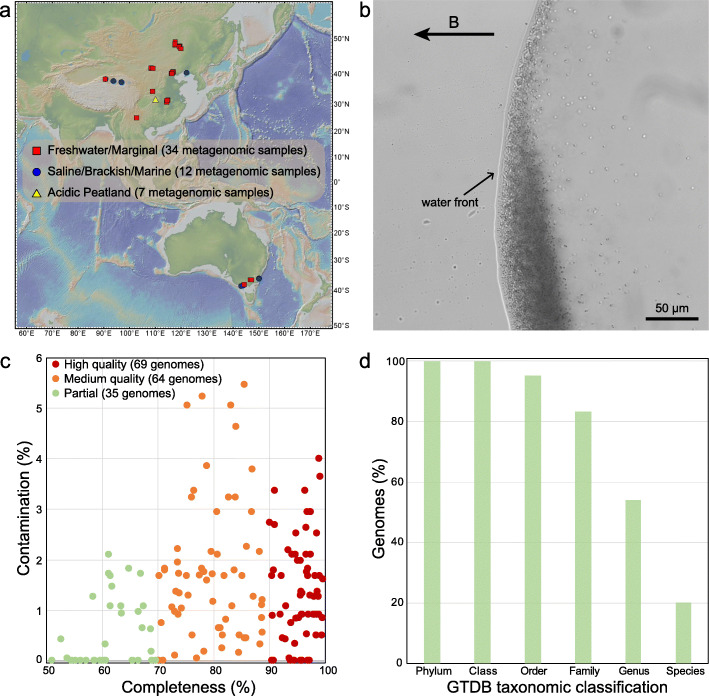
Fig. 2.
Recovery of 168 MTB genomes from various environments. a Map of sampling locations (generated using the GeoMapApp 3.6.0, http://www.geomapapp.org/). Further site details are given in Supplementary Table 1. b A micrograph of MTB cells (cocci and rods) from Lake Dianchi, China, as observed under a light microscope (Olympus BX51, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). The applied field (B) direction is from right to left. c Estimated completeness and contamination of MTB genomes reconstructed in this study. CheckM was used to estimate completeness and contamination. Of these genomes, 69 are high-quality (> 90% completeness and < 5% contamination), 64 are medium-quality (70–90% completeness and < 6% contamination), and 35 are partial (50–70% completeness and < 5% contamination) genomes. d Relative abundance of recovered MTB genomes that can be classified according to the GTDB taxonomy (database Release 04-RS89). Of the 168 recovered genomes, 34 were classified at the species level, 91 were classified at the genus level, 140 were classified at the family level, 160 were classified at the order level, and 168 could be classified at the class and phylum levels. Details are given in Supplementary Table 2