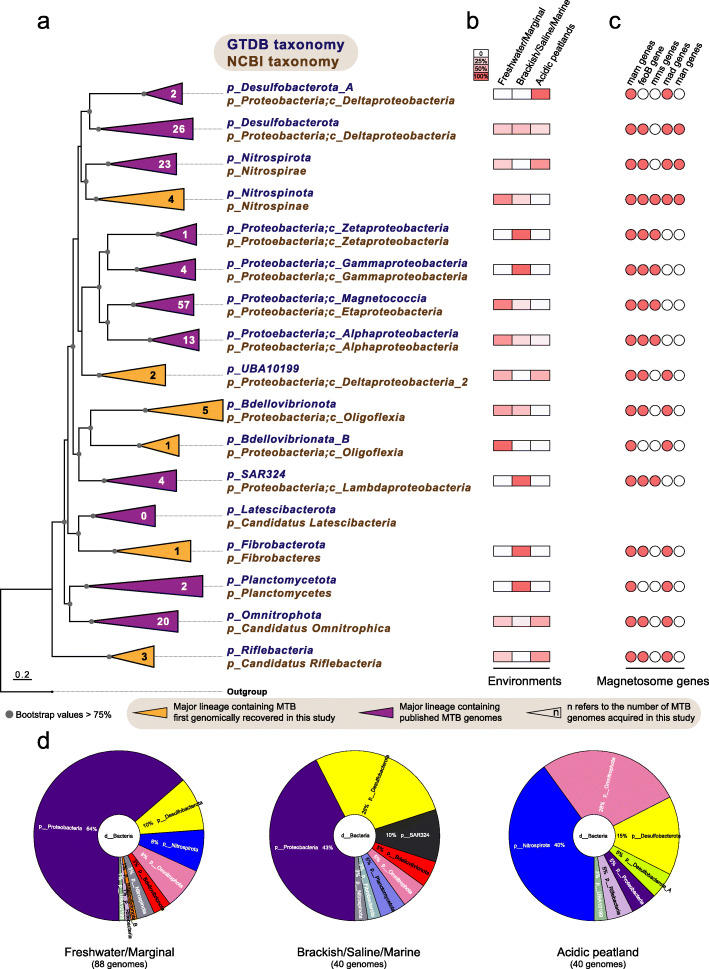
Fig. 3.
Distribution of MTB genomes across Bacterial phyla and distinct environments. a The maximum-likelihood phylogenomic tree of MTB genomes and their close non-MTB relatives inferred from concatenated 120 bacterial single-copy marker proteins [54], which was constructed using IQ-TREE under the LG+I+G4 substitution model. The number in each clade refers to the number of MTB genomes reconstructed in this study. The complete tree is shown in Supplementary Figure 1. b Relative abundances of reconstructed MTB genomes in this study across different environments within each lineage. c Distribution of magnetosome genes (mam, mms, mad, and man) and feoB gene within MGCs across different lineages. d Distribution of acquired MTB genomes at the phylum level across different environments, including freshwater/marginal (< 1 ppt) and saline/brackish/marine (> 1 ppt) sediments, and soils from acidic peatland. Details are given in Supplementary Table 1