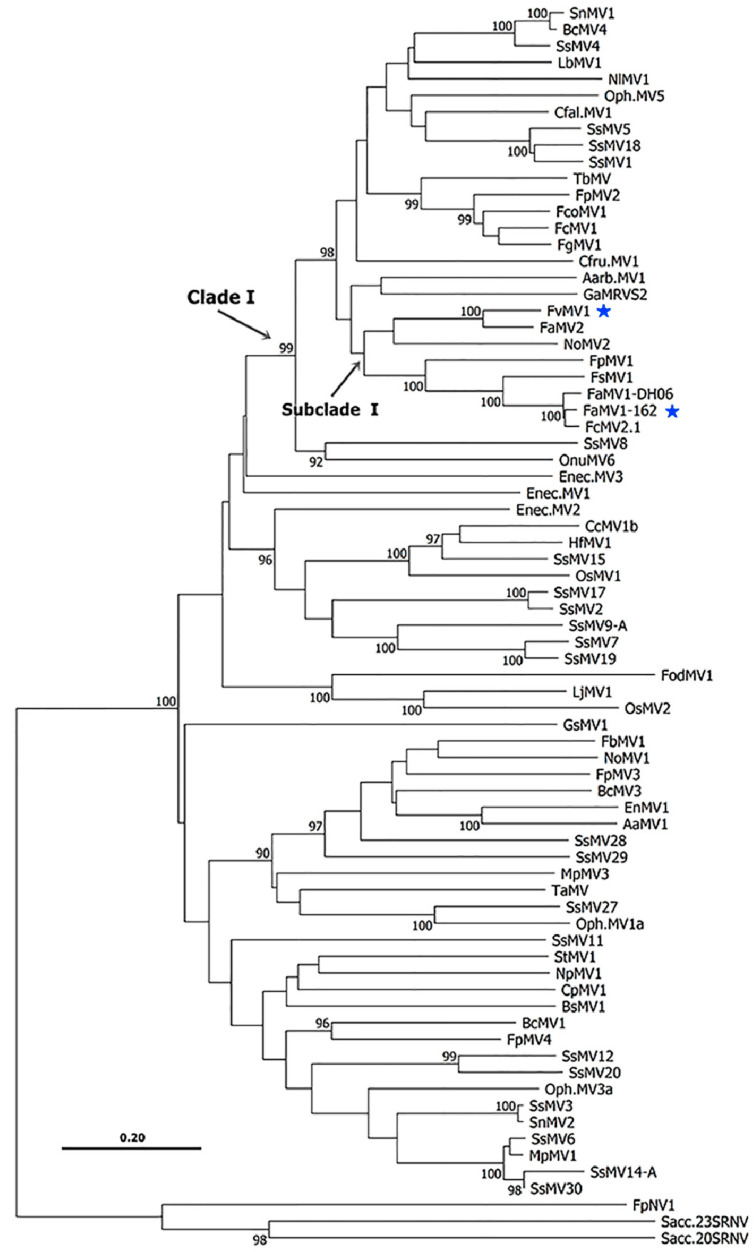
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of mitoviruses (Mitoviridae) isolated from fungi of the Ascomycota phylum. The tree is displayed as a rectangular phylogram of 73 mitoviruses and rooted on the branch to members of the genus Narnavirus (Narnaviridae) as external group (FpNV1: YP_009272902.1, Sacc.20RNV: NP_660178.1 and Sacc.23RNV: NP_660177.1). The tree was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method, based on multiple sequence alignments through MAFTT software (L-INS-i, automatized election). The evolutionary distances were computed using the Poisson correction method (uniform rates between sites), and are in the units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated (complete deletion option). The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) is shown as node labels (values are in percentage and less than 90% were hidden in the graph). The scale bar represents substitutions per site. The viruses identified and characterized in this study are indicated with a blue star.