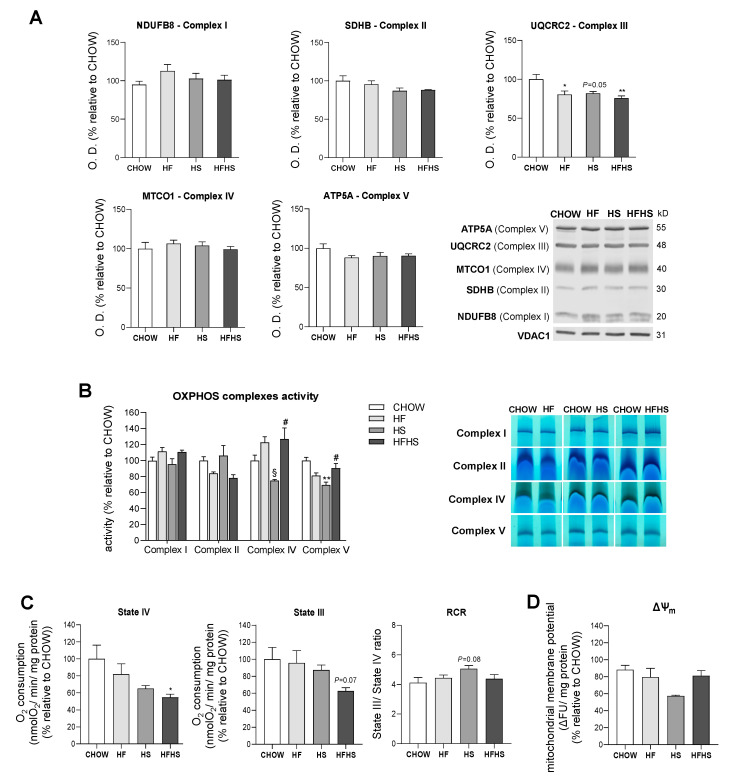
Figure 5.
The HFHS diet decreases mitochondrial respiration. (A) Optical density (arbitrary units) of OXPHOS subunits (NDUFB8, Complex I; SDHB, Complex II; UQCRC2, Complex III; MTCO1, Complex IV; and ATP5A, Complex V) levels and representative Western blot images. VDAC1 was used as a loading control (N = 4). (B) OXPHOS complex activities and in-gel activities representative image (N = 4). (C) Oxygen consumption rate in the basal state (State IV) and in the ADP-stimulated state (State III) and RCR (State III/State IV) (N = 6). (D) Mitochondrial membrane potential (N = 8). All data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. (*) vs. the CHOW diet, (§) vs. the HF diet and (#) vs. the HS diet (P < 0.05); (**) vs. the CHOW diet (P < 0.01); P values were determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test or Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc test. ΔΨm, mitochondrial membrane potential; HF, high-fat; HFHS, high-fat plus high-sucrose; HS, high-sucrose; RCR, respiratory control ratio.