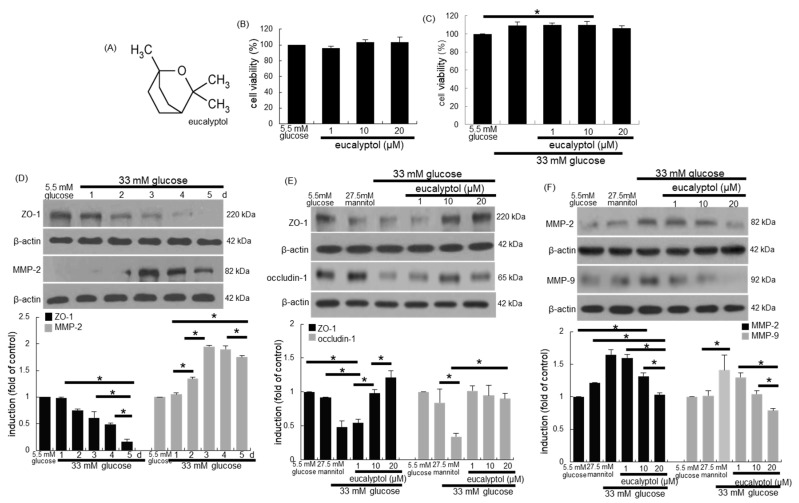
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of eucalyptol (A), toxicity of eucalyptol-treated human retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells (B), inhibitory effects of eucalyptol on proliferation of glucose-exposed RPE cells (C), temporal responses of epithelial induction of ZO-1 and MMP-2 (D) and effects of eucalyptol on tight junction proteins of ZO-1, occludin-1, MMP-2 and MMP-9 injured by glucose (E and F). An MTT assay was conducted for measurement of cell viability (B and C, 100% viability with 5.5 mM glucose control). Bar graphs for viability (mean ± SEM, n = 5) was expressed as the percentage of cell survival, compared to the glucose control. Cell lysates were subject to western blot analysis with a primary antibody against ZO-1, occludin-1, MMP-2, MMP-9 and β-actin for a cellular internal control (D–F). Bar graphs (mean ± SEM, n = 3) in the panels represent densitometric results of blot bands. * Values in respective bar graphs indicate a significant difference at p < 0.05.