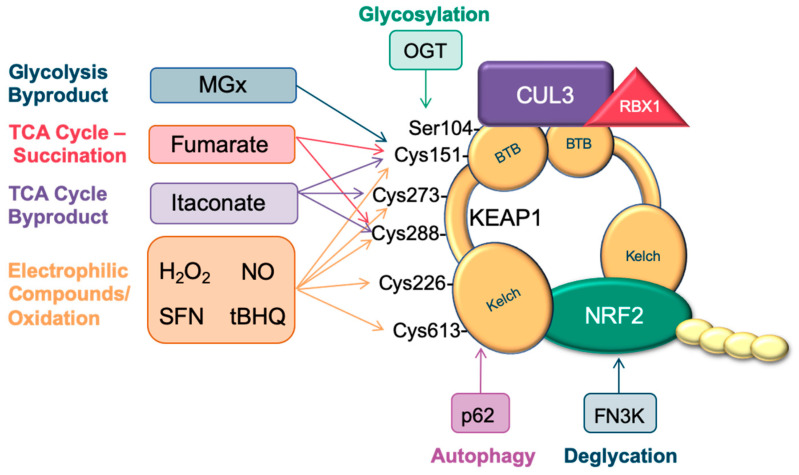
Figure 3.
NRF2 is activated by oxidants, signaling molecules, and metabolites. KEAP1: KEAP1 is glycosylated by O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) at serine 104. The glycolysis byproduct methylglyoxal (MGx) mediates a crosslink between cysteine 151 with arginine 135, activating the NRF2 transcriptional program. Further, NRF2 activation can result from fumarate-mediated succination of cysteines 151 and 288. The TCA cycle byproduct itaconate can also activate NRF2 by reacting with cysteines 151, 273, and 288. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), nitric oxide (NO), sulforaphane (SFN), and tert-butyl hydroquinone (tBHQ) can activate NRF2 by modifying cysteine residues 151, 273, 288, 226, and 613. The autophagy adaptor sequestome 1, p62, activates NRF2 by binding to the Kelch domain region of KEAP1. NRF2: NRF2 is destabilized by glycation, which is reversed by the enzyme Fructosamine-3-kinase (FN3K).