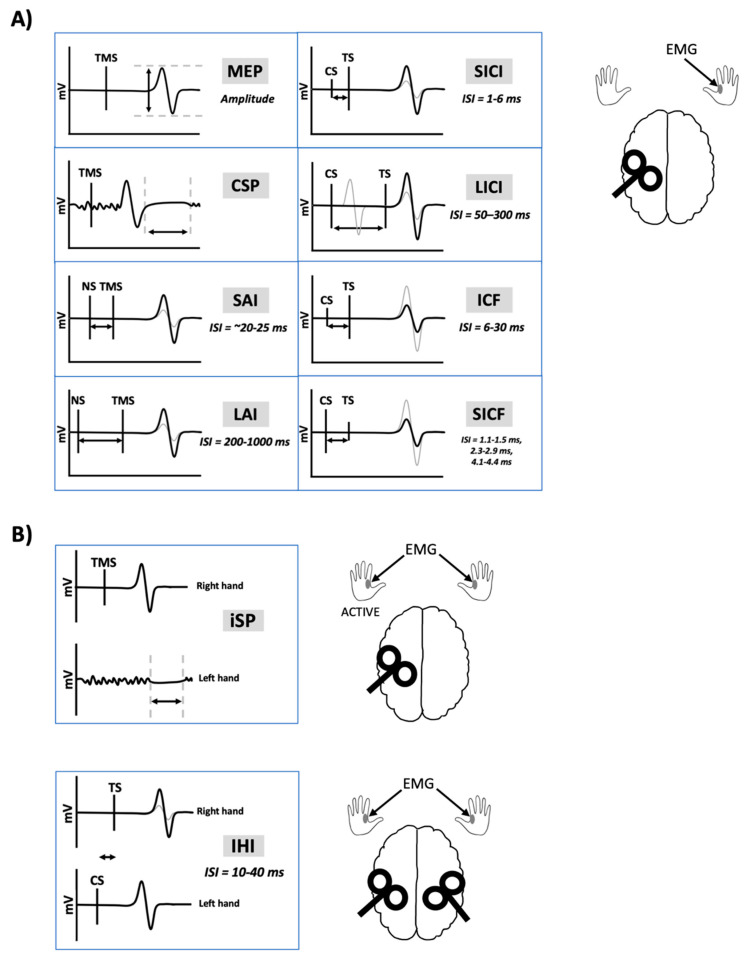
Figure 1.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation-electromyography (TMS-EMG) outcome measures. Black lines indicate traces following a single pulse of TMS. Grey lines indicate traces following nerve stimulation (NS) and TMS paired together or following a conditioning stimulus (CS) and test stimulus (TS) pair. (A) Unilateral measures. TMS delivered to the left motor cortex results in a motor-evoked potential (MEP) recorded from a muscle in the right-hand using EMG. Delivering TMS during isometric contraction of the right-hand muscle leads to an interruption of voluntary contraction known as the cortical silent period (CSP). Short-latency afferent inhibition (SAI) and long-latency afferent inhibition (LAI) occurs when electrical peripheral NS is delivered prior to the TMS pulse, at interstimulus intervals (ISIs) of 20–25 ms or 200–1000 ms, respectively. Short-interval intracortical inhibition (SICI) is measured when a subthreshold CS is delivered 1–6 ms prior to a suprathreshold TS. The resulting MEP is inhibited, compared to the MEP obtained following the TS alone. Long-interval intracortical inhibition (LICI) is measured when a suprathreshold CS is delivered 50–300 ms prior to a suprathreshold TS, leading to inhibition of the MEP. Intracortical facilitation (ICF) is measured when a subthreshold CS is delivered 6–30 ms prior to a suprathreshold TS, leading to facilitation of the MEP. Short-interval intracortical facilitation (SICF) is measured when a suprathreshold CS is delivered 1.1–1.5 ms, 2.3–2.9 ms, or 4.1–4.4 ms prior to a subthreshold TS, leading to facilitation of the MEP. (B) Transcallosal measures. Delivering TMS to the left motor cortex during isometric contraction of the left-hand muscle leads to an interruption of voluntary contraction known as the ipsilateral silent period (iSP). Interhemispheric inhibition (IHI) is measured when a suprathreshold CS is delivered to the right motor cortex prior to a suprathreshold TS delivered to the left motor cortex, leading to inhibition of the MEP. Short-latency IHI (SIHI) occurs at ISIs of ~10 ms and long-latency IHI (LIHI) occurs at ISIs of ~40 ms.