FIGURE 1.
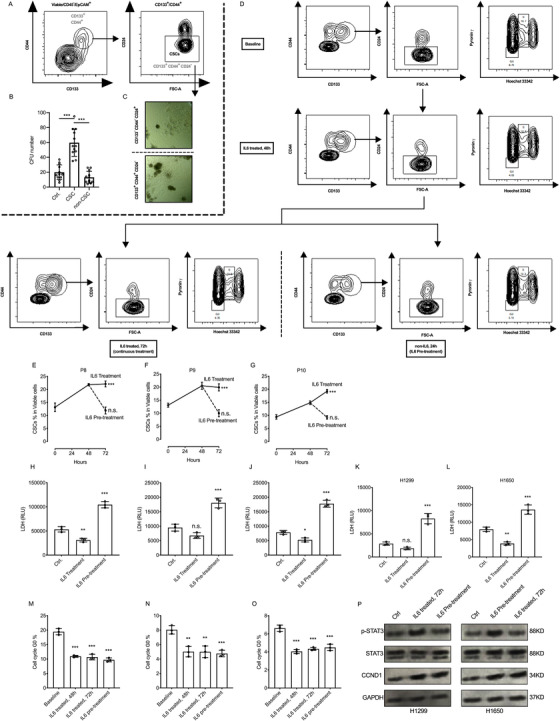
The activated IL6‐STAT3 pathway (but not cell cycle pathway) closes rapidly upon the loss of IL6 signaling and contributes to the chemosensitivity in IL6 pretreatment. A, FACS and sorting strategy for lung cancer stem cells; CD133+, CD44+, and CD24− lung cancer cells (P1, P3, P4, and P7) were gated and sorted as cancer stem cells (CSCs). B, Primary lung cancer cells were sorted to CSCs (CD133+/CD44+/CD24−), non‐CSCs (CD133−/CD44−/CD24+) and control (cells sorted without selection) subgroups for colony formation assay in Matrigel. Compared with control and non‐CSC group, CSC groups have the advantage of forming more colonies. CFU, colony formation unit. C, CD133+, CD44+, and CD24− cancer stem cells were seeded in Matrigel for colony formation assay, the example pictures showed the morphology difference of colonies originated from cancer stem cells or non‐cancer stem cells. Cancer stem cells have the advantage of forming bigger dense colonies. D, The FACS plots and FACS flowchart of primary lung cancer cells (PLCC), the cells were treated with IL6 (2 ng/ml) for 48 hours, after that lung cancer cells were cultured in medium with or without IL6 (2 ng/ml) for another 24 hours. Then, cells were collected for CSC staining and cell cycle staining. E‐G, The percentages of CSC population were measured at baseline, at 48 hours and 72 hours. Compared to baseline, in primary lung cancer cells (P8, P9, and P10) at 48 hours, the CSC population were expanded. At 72 hours, the CSC population remain expanded (or kept expanding in P10) in IL6 continues treatment groups, while the percentages of CSC population decreased rapidly (to the baseline level) in IL6 pretreatment groups. H‐L, The primary lung cancer cells (P8, P9, and P10) and lung cancer cell lines (H1299 and H1650) were treated with IL6 (2 ng/mL) for 48 hours, then reseeded with same cell number, after that cDDP was added to the medium (5 μM final concentration) with or without IL6 (2 ng/mL) for 24 hours (for control group, no IL6 was added for 72 hours), next the supernatants were collected for cell death measurements. We found the continues IL6 treatment protect lung cancer cells from death during chemotherapy, but IL6 pretreatment contributes to the chemosensitivity compared to the control group. M‐O, Same experimental settings to (B‐D), and the percentages of G0 population were measured at baseline, at 48 hours and 72 hours. Compared to the baseline, the IL6 treatment significantly decreased the G0 populations, and upon the loss of IL6 signaling, the G0 population remained similar to 48 hours group. P, The western blots of STAT3 pathway and cell cycle indicator (cyclin D1) in H1299 and H1650 cells, (Control group), cells without treatment for 72 hours. (IL6 treated, 72 hours group), Cells treated with IL6 (2 ng/mL) for 72 hours. (IL6 pretreatment group), Cells treated with IL6 (2 ng/mL) for the first 48 hours, then fresh medium was changed for the next 24 hours. The protein samples were harvested for western blot, our data indicated the rapidly close of STAT3 pathway without continuous IL6 treatment, but interestingly, the CCND1 level remains high in IL6 pretreatment group compared to the baseline level
