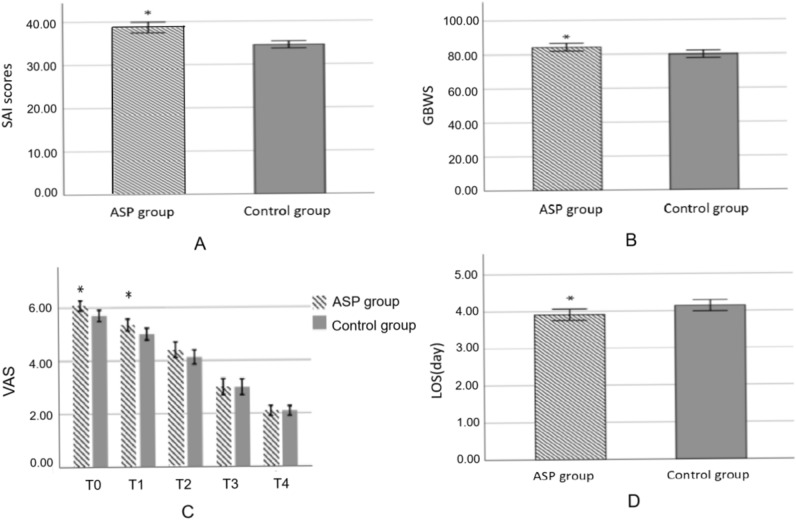
Figure 2.
(A) SAI scores after interactive communication with anesthetists, patients exhibited significantly higher levels of SAI scores after interactive communication with their attending anesthetist (39.72 ± 6.27 versus 34.56 ± 4.46, P < 0.05); (B) GBWS after surgery, patients in the ASP group had higher scores in the General well-being test when compared with those in the Control group (84.25 ± 11.72 vs. 79.86 ± 11.53, P < 0.05); (C) VAS scores after surgery, Patients’ postoperative pain level measured by VAS scores showed significant differences between the two groups immediately after surgery (6.08 ± 1.01 vs. 5.70 ± 1.13, P < 0.05) and 12 h after surgery (5.46 ± 1.20 vs. 5.00 ± 1.18, P < 0.05), while there was no significant difference between the two groups at 24 h, 36 h and 48 h after surgery (4.41 ± 1.52 vs. 4.13 ± 1.43, P = 0.164; 3.00 ± 1.57 vs. 2.99 ± 1.59, P = 0.967; 2.09 ± 1.00 vs. 2.09 ± 0.98, P = 0.975); (D) Comparison of length of stay in hospital, Patients in the ASP group had shorter hospital stay compared to those in the Control group (3.91 ± 0.79 vs. 4.14 ± 0.79, P = 0.031).