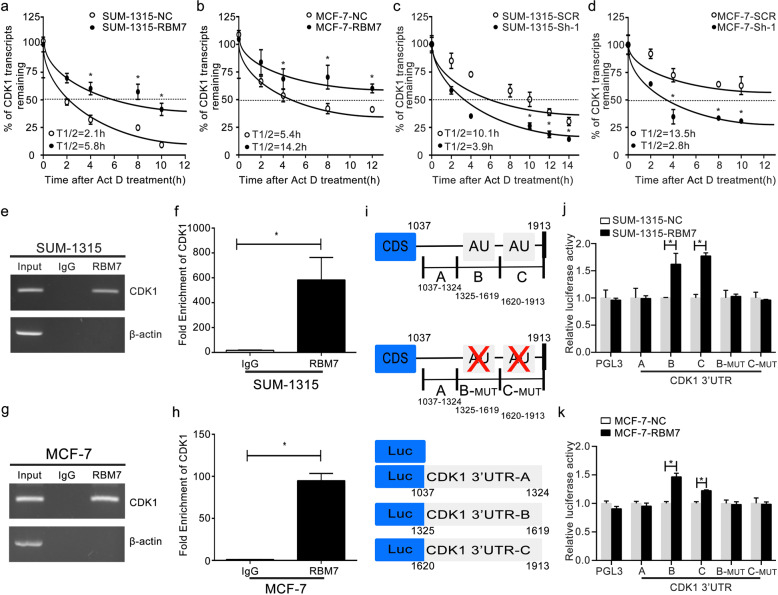
Fig. 5. RBM7 directly bound to the 3′-UTR of CDK1 mRNA to stabilize the CDK1 transcript.
a, b The half-life of CDK1 transcript was increased after RBM7 overexpression in SUM-1315 (a) and MCF-7 (b) cells. The control (NC) and RBM7 overexpression (RBM7) cells were treated with 5 µg/ml Act D for 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 14 h. c, d The half-life of CDK1 transcript was decreased after RBM7 knockdown in SUM-1315 (c) and MCF-7 (d) cells. The control (SCR) and RBM7 knockdown (Sh-1) cells were treated with 5 µg/ml Act D for 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 14 h. The relative quantification was calculated by the 2−ΔΔCt method and normalized based on β-actin. e, f SUM-1315 and g, h MCF-7 cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with RBM7 antibody. PCR (e, g) and RT-qPCR (f, h) measured transcript levels of CDK1 and β-actin within RBM7 or IgG immunocomplexes in MCF-7 and SUM-1315 cell lysates (*P < 0.05). i Schematic diagram of various regions in the 3′-UTR of CDK1 mRNA. j, k The reporter containing CDK1 3′-UTR-B, C was increased by overexpression of RBM7 in SUM-1315 (j) and MCF-7 (k) cells. Data were shown as mean ± SD (*P < 0.05).