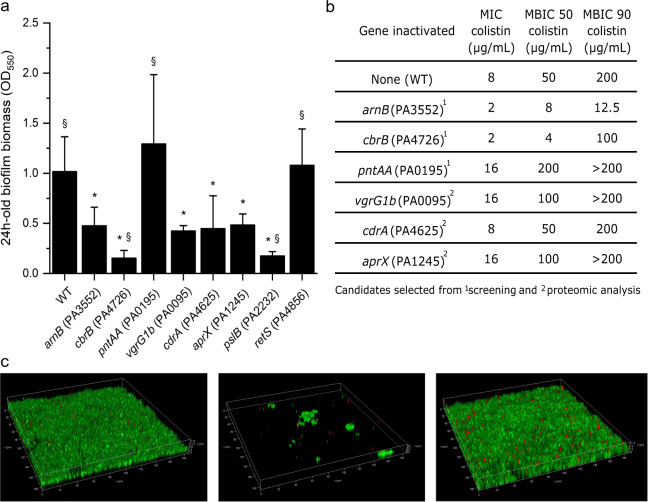
Fig. 5. Confirmation of the phenotypes identified in our screening.
a Biofilm formation was quantified after 24 h incubation in M9 medium by crystal violet staining (average of at least 18 wells from two independent cultures). The pslB and retS mutants were used as a reference for low and high biofilm formation, respectively. The cbrB and pntAA mutants demonstrated substantially reduced and increased biofilm formation, respectively. Symbols (* and §) indicate significant differences (Student’s tests with p value < 0.001) in comparison to MPAO1 WT and the arnB mutant, respectively. PAO1 genes are shown in brackets, the respective MPAO1 genes are mentioned in the text. b Resistance of planktonic and biofilm cells towards colistin was evaluated for a subset of mutant strains identified in the screening (1) or based on differential proteomics abundance (2). The MIC was determined as the lowest concentration resulting in a 90% reduction of bacterial growth after 24 h in M9 medium compared to the non-treated condition (average of four replicates from two independent cultures). The MBIC was determined as the lowest concentration resulting in a 50% or 90% reduction of the biofilm cell recovery after 24 h treatment compared to the non-treated condition (average of four replicates from two independent cultures). c Comparative confocal micrographs after live/dead staining (green – live cells stained with Syto9; red – dead cells stained with propidium iodide) of 18 h MPAO1 WT, cbrB and arnB biofilms grown under microfluidic conditions using the publicly available mold confirm reduced biofilm formation for the cbrB mutant and robust biofilm formation of the arnB mutant in the absence of treatment.