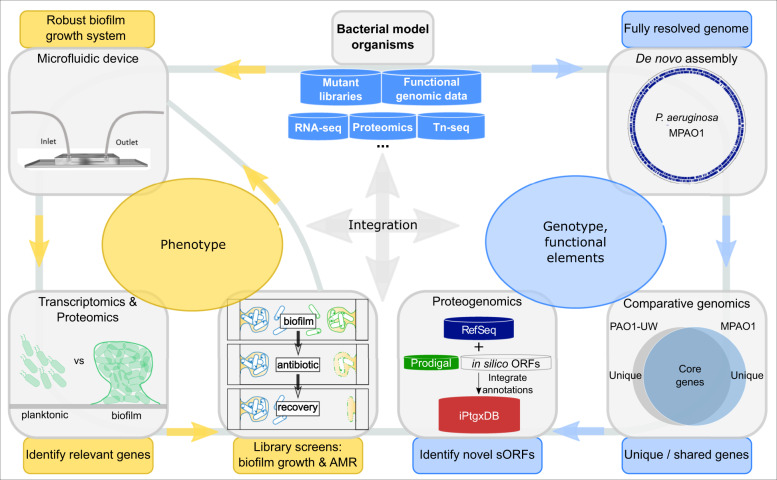
Fig. 7. Integrated model system to identify and validate genes relevant for biofilm growth and AMR.
A sequential genomics-driven workflow (blue arrows) to de novo assemble the complete genome, identify unique and conserved genes among key reference strains by comparative genomics and missed genes by proteogenomics is integrated with an experimental workflow in the form of an iterative cycle that can be entered at various points (yellow arrows). This workflow allows the study of biofilm grown cells, to explore differentially abundant genes or proteins compared to planktonic cells, and to screen mutant libraries to identify functionally relevant genes. The model leverages the enormous value of genetic resources like gene knockout or transposon insertion mutant libraries and functional genomics data sets (RNA-seq, Tn-seq, etc.; blue containers). Additionally, it allows for phenotypic characterization of biofilms formed by mutant strains, thereby allowing us to determine the impact of specific genes on biofilm formation and assess their role in AMR (yellow arrows).