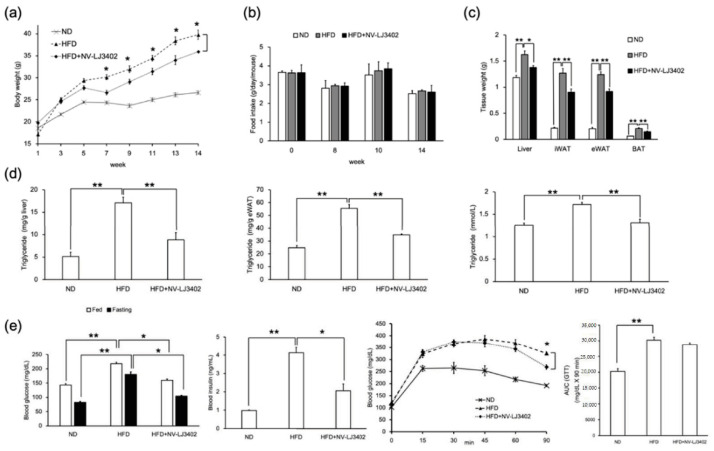
Figure 1.
Non-viable Lactobacillus johnsonii JNU3402 (NV-LJ3402) attenuates diet-induced obesity in high fat diet (HFD)-fed mice. Seven-week-old C57BL/6J male mice were administered NV-LJ3402 or Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) daily for 14 weeks during feeding with a normal diet (ND) or an HFD, and body weight gain (a) of mice was measured as indicated. (n = 7 per group). HFD vs. HFD+NV-LJ3402, * p < 0.05. Daily Food intake (b) was measured three times per indicated week, and tissue weights at the 14th week of feeding (c) were measured (B‒C, n = 6–7 per group). (d) Triglyceride (TG) levels in the tissues (liver and epididymal WAT (eWAT)) and plasma (n = 6–7 per group). (e) Plasma glucose, insulin levels, and glucose tolerance test results from each group of mice after 14 weeks of feeding (n = 7 per group). All data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. ND vs. HFD, HFD vs. HFD+NV-LJ3402, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.