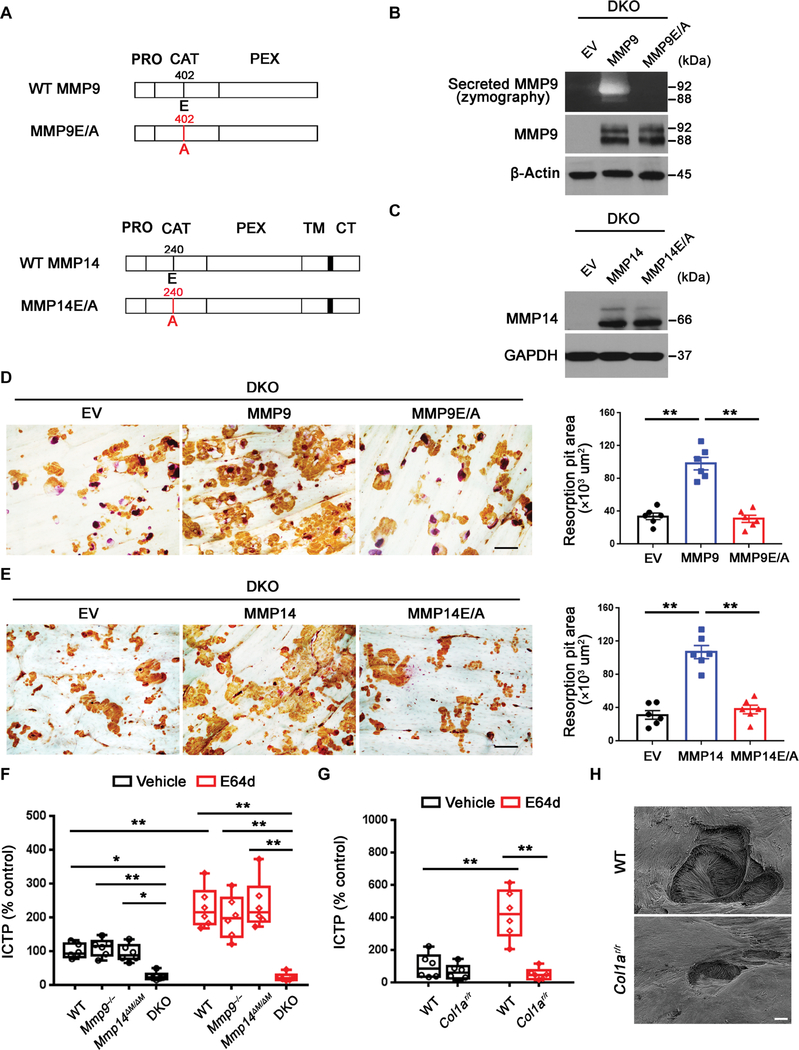
Fig. 4. Mmp9/Mmp14 catalytic activity codetermines osteoclast-mediated bone resorption by proteolyzing bone type I collagen.
(A) A schematic diagram of full-length human MMP9 and MMP14 and their respective catalytically inactive mutants depicting the pro (PRO), catalytic (CAT), hemopexin (HPX), transmembrane (TM) domains, and cytosolic tail (CT). (B) DKO BMDMs were transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing full-length MMP9, an MMP9E/A mutant, or an empty control (EV) and differentiated into osteoclasts. Supernatant and cell lysate were collected for gelatin zymography and MMP9 immunoblots, respectively. (C) DKO BMDMs were transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing full-length MMP14, MMP14E/ A, or an empty control (EV) and differentiated into osteoclasts. Cell lysates were collected for MMP14 immunoblotting. (D) MMP9 or MMP9E/A-transduced BMDMs were induced into osteoclasts and cultured atop bone slices for 3 days. Osteoclasts were removed, resorption pits were visualized by WGA-DAB staining, and resorption pit area was quantified (n = 6). Scale bar, 100 μm. (E) MMP14 or MMP14E/A-transduced BMDMs were induced into osteoclasts and cultured atop bone slices as described in (D). Resorption pits were visualized by WGA-DAB staining, and resorption pit area was quantified (n = 6). Scale bar, 100 μm. (F) Osteoclasts differentiated from wild-type, Mmp9−/−, Mmp14ΔM/ΔM, or DKO BMDMs were cultured atop decalcified cortical bone slices with or without E64d (20 μM) for 3 days, and supernatants were collected for ICTP ELISA (n = 6). (G) Wild-type osteoclasts were cultured atop normal or Col1ar/r mutant bone with or without E64d for 3 days, and supernatants were collected for ICTP ELISA (n = 6). (H) Resorption pits generated on normal or Col1ar/r bone by wild-type osteoclasts ex vivo were imaged by scanning electron microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. All results are representative of data generated in at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Error bars are means ± SEM. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA (D and E) or two-way ANOVA (F and G) with Bonferroni correction.