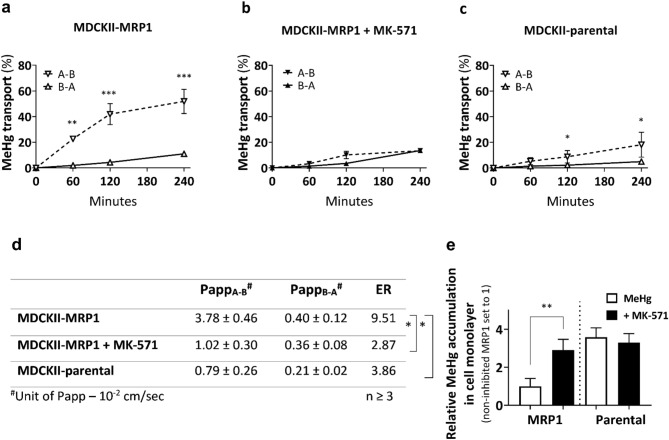
Fig. 2.
MeHg transport across MDCKII-parental and MDCKII-MRP1 cells over 4 h. a Predominant transport of MeHg in the apical-to-basolateral (A–B) direction in MDCKII-MRP1 cells. b MRP1 inhibitor MK-571 (50 µM) decreased A–B MeHg transport in MDCKII-MRP1 cells. c MDCKII-parental cells show reduced A–B MeHg transport than MDCKII-MRP1 cells. d Values of permeable coefficient (Papp) were calculated at 120 min within linear phase of MeHg transport. Statistical significance between efflux ratios (ER = PappA-B/PappB-A) of MeHg transport in MDCKII-MRP1 (ER = 9.51), MDCKII-MRP1 + MK-571 (ER = 2.87) and MDCKII-parental cells (ER = 3.86) revealed MeHg as MRP1 substrate. e Retention of MeHg in cell monolayer after transport assay. Data are presented as means ± SD (n ≥ 3). Statistical significance was evaluated by parametric student’s t-test (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001)