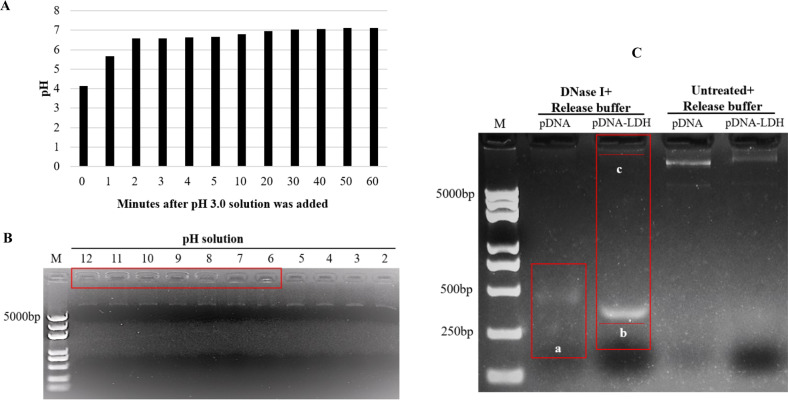
Fig. 2. Stability of pDNA on layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanosheets examined by acidic and enzymatic treatments.
a pH value dynamics over 60 min from the introduction of diluted nitric acid (pH 3.0) to LDH solution. The pH increased from acidic to basic values within 60 min from the introduction of diluted nitric acid (pH 3.0) to LDH solution. The initial pH of 3.0 quickly changed in the first several minutes and stabilized at pH 7.12 after 1 h, indicating dissolution of LDH under acidic conditions. b pDNA–LDH was suspended in solutions at a range of initial pH values (2.0–12.0) and incubated for 24 h. pDNA release was complete in pH ≤ 5.0 solutions. At pH ≥ 6.0, most of the pDNA loaded on LDH nanosheets did not migrate on the gel during electrophoresis, as indicated by the florescence being retained in the well. M = 5 kb DNA ladder. c Treatment of pDNA and pDNA–LDH with DNase I. Gel electrophoresis showed that the treated pDNA was released from the LDH nanosheets and almost completely degraded (a). The treated pDNA–LDH showed that a part of the DNA was released from the LDH nanosheets and incompletely degraded (b). The other pDNA was released from the LDH nanosheets without degradation, which was indicated by the florescence being retained near the well (c). M = 5 kb DNA ladder. pDNA–LDH: pDNA loaded on LDH nanosheets, pDNA: plasmid DNA