Fig. 2.
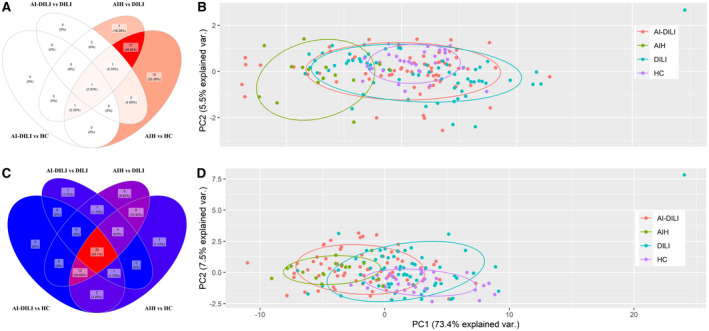
Patients with AI‐DILI showed significant increased IgM autoantibodies but not IgG autoantibodies.(A) Venn diagram showing one elevated IgG autoantigen observed in comparisons of AI‐DILI versus HCs and AI‐DILI versus DILI. Twenty‐four autoantigens were observed between de novo AIH versus HCs and de novo AIH versus DILI controls. (B) PCA of combined IgG autoantibodies showing clustering of de novo AIH compared to the other three groups (pairwise Adonis test with adjusted P values for FDR: de novo AIH versus HCs, P < 0.01; de novo AIH versus DILI, P < 0.01; de novo AIH versus AI‐DILI, P < 0.01; differences between HCs, DILI, and AI‐DILI by autoimmunity status were not statistically significant). (C) Venn diagram showing 25 elevated IgM antigens recognized all by de novo AIH versus HCs, de novo AIH versus DILI, AI‐DILI versus HCs, and AI‐DILI versus DILI. (D) PCA of combined IgM autoantibodies showing clustering of de novo AIH/AI‐DILI difference from HC/DILI (pairwise Adonis test with adjusted P values for FDR: de novo AIH versus HCs, P < 0.01; de novo AIH versus DILI, P < 0.01; AI‐DILI versus HCs, P < 0.01; AI‐DILI versus DILI, P < 0.01; differences between de novo AIH and AI‐DILI (P = 0.078) by autoimmunity status were not statistically significant). Abbreviations: FDR, false discovery rate; var., variance.
