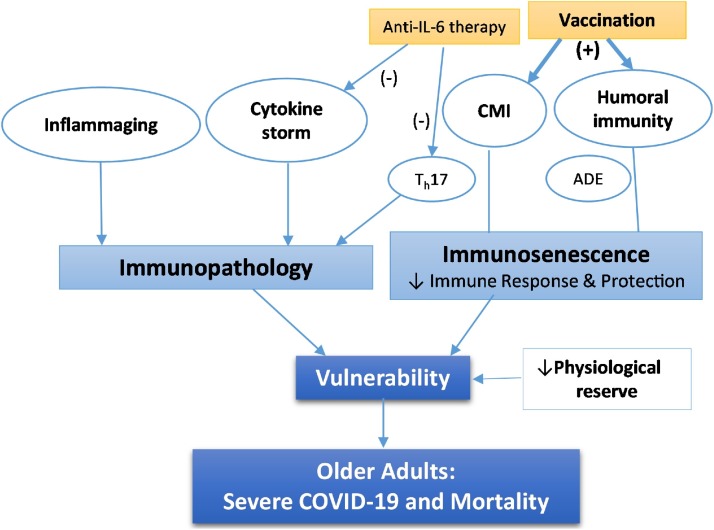
Fig. 5.
The immune hypothesis. This hypothesis encompasses age-related impairment of immune response and protection against SARS-CoV-2 and immunopathology. Immune response includes humoral immunity (i.e., antibody response) and cell-mediated immunity (CMI) (right). While age-related immunosenescence is believed to weaken immune protection, vaccination enhances it. Inflammaging and cytokine storm may lead to Immunopathology (left). Not all immune responses are protective as antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) in humoral immunity may promote SARS-CoV-2 infection while Th17 response in CMI may contribute to cytokine storm. Anti-IL-6 therapy with monoclonal antibodies against either IL-6 or IL-6 receptor currently in clinical trials can block cytokine storm and its downstream event and/or suppress Th17 response. Age-related decrease of physiological reserve in respiratory and other organ systems may also contribute to vulnerability. Together, they lead to disproportionately severe COVID-19 and high mortality in older adults.