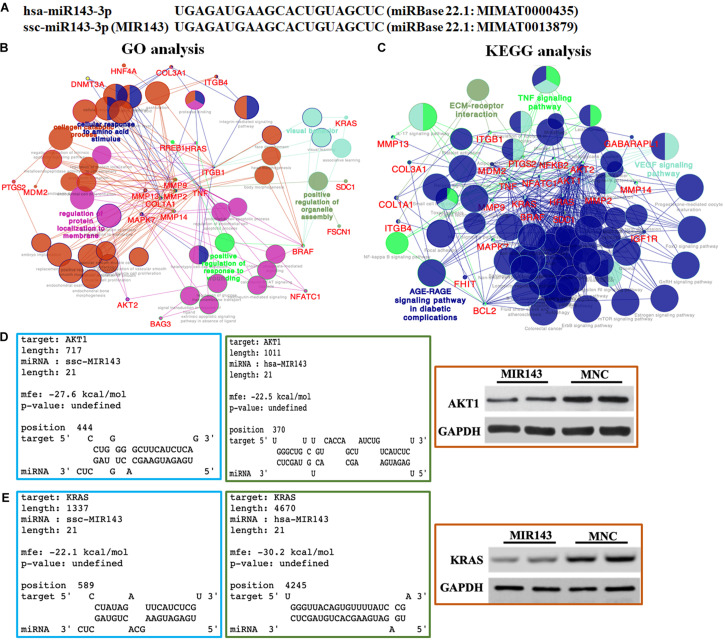
FIGURE 3.
Bioinformatic prediction and functional analysis of MIR143 candidate targets. (A) Sequence alignment of human hsa-miR-143-3p and pig MIR143. (B) GO pathway analysis of hsa-miR-143-3p experimentally validated targets (MIR143 candidate genes). (C) KEGG pathway analysis of hsa-miR-143-3p experimentally validated targets (MIR143 candidate genes). (D) Predicted results from the RNAhybrid website (https://bibiserv.cebitec.uni-bielefeld.de/rnahybrid/) showed the possibility of hsa-miR-143-3p binding to human AKT1 (verified, blue box) and pig MIR143 binding to pig AKT1 (predicted, green box). Further, Western blotting (WB) showed the AKT protein expression when MIR143 was overexpressed in porcine GCs (red box, MNC indicated MIR143 mimic negative control). (E) Predicted results from the RNAhybrid website (https://bibiserv.cebitec.uni-bielefeld.de/rnahybrid/) showed the possibility of hsa-MIR143 binding to human KRAS (verified, blue box), and MIR143 binding to pig KRAS (predicted, green box). Further, WB showed the effect on KRAS protein expression when MIR143 was overexpressed in porcine GCs (red box, MNC indicated MIR143 mimic negative control).