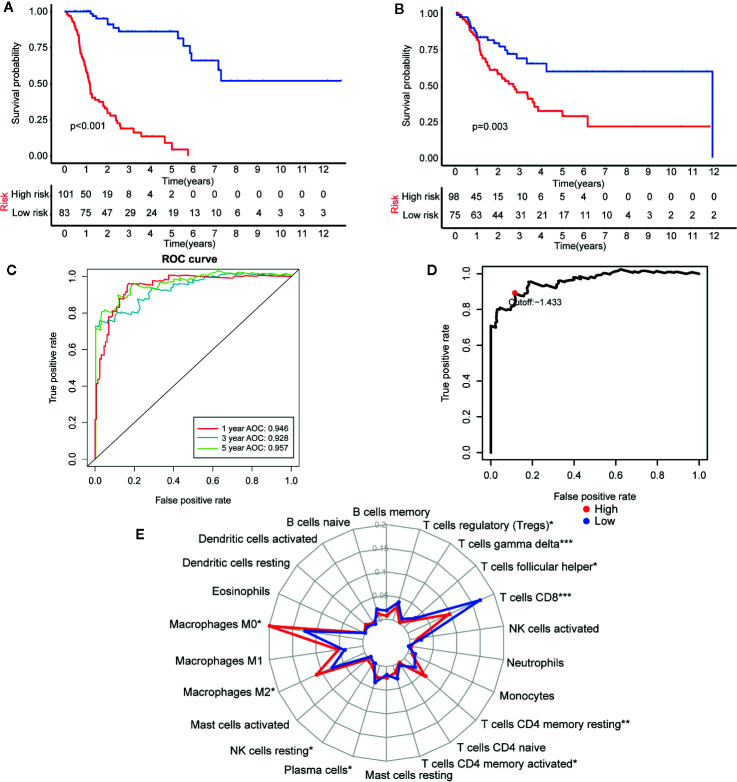
Figure 9.
Establishment and assessment of the IRGP-OBS. (A) According to the OBS curve, OBS was poorer for the high risk group as compared to the low risk group in the training cohort (p < 0.001). (B) According to the OBS curve, OBS was poorer for the high risk group as compared to the low risk group in the training cohort (p = 0.003). (C) The AUCs for 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS in the training cohort were 0.946, 0.928, and 0.957, respectively. (D) A time-dependent ROC curve for IRGP-OBS in the training and testing dataset. An IRGP score of −1.433 was used as a cut-off to assign patients to the high- or low-risk group. (E) The abundances of M0 macrophages (p = 0.013), M2 macrophages (p = 0.049), T cells CD4 memory resting (p = 0.001) and NK cells resting (p = 0.035) were significantly greater in the high risk group, while the abundances of CD8+ T cells (p < 0.001), plasma cells (p = 0.043), follicular helper T cells (p = 0.025), gamma delta T cells (p < 0.001), T cells regulatory (p = 0.019), T cells CD4 memory activated (p = 0.011) were significantly enriched in the low risk group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (t-test).