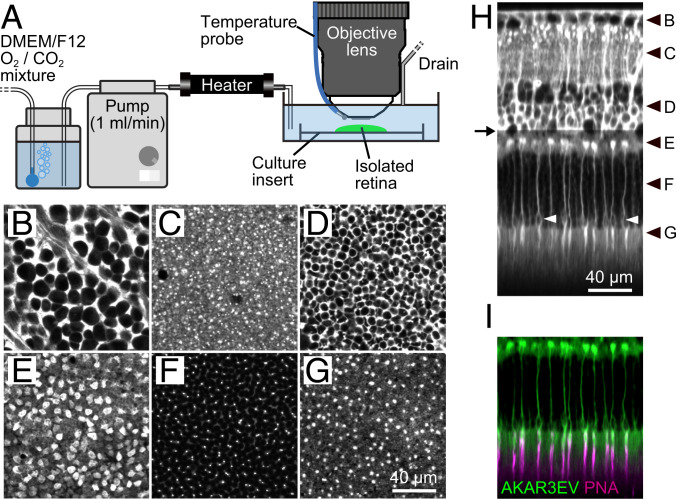
Fig. 1.
Two-photon imaging of the PKAchu retina. (A) Imaging setup. The isolated PKAchu retina was flat mounted on a culture insert, perfused with DMEM/F12 medium, and imaged using an upright two-photon microscope with a water immersion objective lens. (B–G) Fluorescent images obtained from the PKAchu retina at the ganglion cell layer (GCL; B), inner plexiform layer (IPL; C), inner nuclear layer (INL; D), outer plexiform layer (OPL; E), outer nuclear layer (ONL; F), and photoreceptor segments layer (PRS; G). Images were obtained by averaging FRET-donor channel (CFP Ch) and FRET-acceptor channel (FRET Ch) images. (H) Longitudinal view of the PKAchu retina. The image was reconstructed from z-stack images (214 planes with 1 µm z intervals). White arrowheads indicate cone nuclei. Black arrowheads indicate z positions of the cross-sectional images in B–G, and an arrow indicates the z position from which the excitation laser power was attenuated to avoid detector saturation. (I) Cone labeling with rhodamine labeled peanut agglutinin (PNA-rhodamine) (magenta) overlaid with AKAR3EV signals (green).