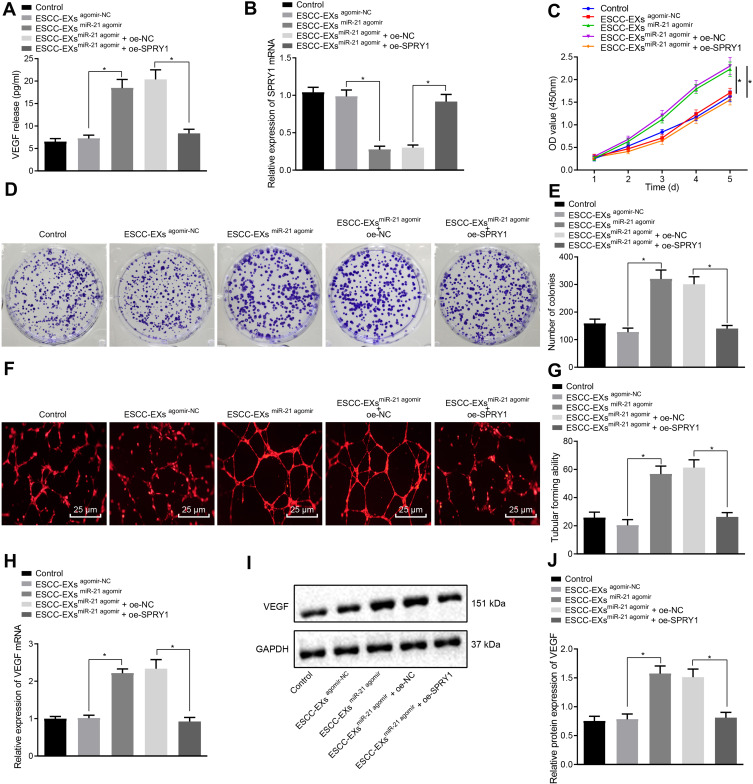
Figure 6.
Exosome-encapsulated miR-21 released from ESCC cells represses SPRY1 and expedites HUVEC proliferation and angiogenesis via VEGF upregulation. ESCC cells were infected with the miR-21 agomir, agomir-NC, control, miR-21 agomir + oe-SPRY1 or miR-21 agomir + oe-NC. (A) The expression pattern of VEGF after co-culture of exosomes and HUVECs as determined by ELISA. (B) The mRNA expression pattern of SPRY1 following the co-culture of exosomes and HUVECs as measured using RT-qPCR. (C) The proliferation of HUVECs assessed using CCK-8. (D, E) Colony formation ability of HUVECs assessed using colony formation assay. (F) Tube formation of HUVECs assessed using tubular formation assay observed under an inverted microscope (scale bars = 25 µm). (G) Tube formation of HUVECs assessed using tubular formation assay (VEGF: 151 kDa). (H) The mRNA expression pattern of VEGF in HUVECs as assessed by RT-qPCR. (I, J) The protein expression pattern of VEGF in HUVECs as assessed by immunoblotting. *p < 0.05 vs controls. Comparisons among multiple groups were conducted by one-way ANOVA, followed by the Tukey’s post hoc test (A, B, E, G, H, and (J). Statistical analysis in relation to time-based measurements within each group was realized using repeated measures ANOVA, followed by the Bonferroni’s post hoc test (C). The experiment was conducted three times independently.