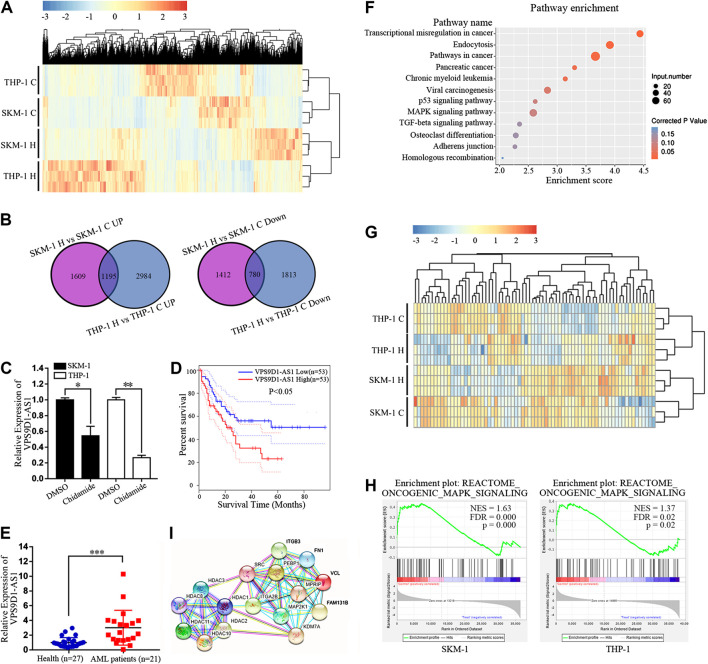
FIGURE 3.
Chidamide regulates the expression of lncRNAs and inhibits the oncogenic MAPK signaling pathway in AML cells. (A) Cluster analysis of lncRNAs differentially expressed in Chidamide-treated group and control group. Whether the cells were treated with Chidamide at 1,000 nM for 48 h. (B) 1,195 lncRNAs were co-upregulated and 780 lncRNAs were co-downregulated were observed. (C) Expression of VPS9D1-AS1 in the Chidamide-treated group and the control group analyzed by qRT-PCR. Each bar presents mean ± SD from three independent experiments * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (D) Overall survival was analyzed and compared by Kaplan-Meier. Patients with high (lncRNA VPS9D1-AS1 high, n = 53) vs. low (lncRNA VPS9D1-AS1 low, n = 53). (E) Polymerase chain reaction analysis of lncRNA VPS9D1-AS1 expression in patients with de novo AML (n = 21) vs. health control people (n = 27). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. (F) Pathway enrichment analysis showing genes involved in MAPK signaling pathway were significantly enriched. (G) Cluster analysis was performed on genes related to the oncogenic MAPK signal. (H) GSEA showed that oncogenic MAPK signaling was down-regulated in Chidamide-treated AML cells. (I) Protein network analysis revealed top 10 of the enriched oncogenic MAPK signal proteins were closely connected to HDAC1/2/3/8/10/11.