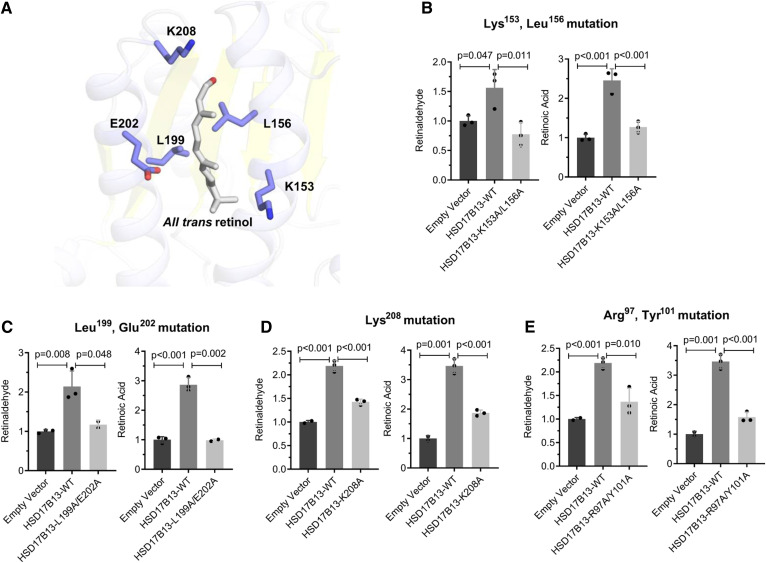
Fig. 5.
The amino acid residues in the putative substrate binding sites Lys153, Leu156, Leu199, Glu202, Lys208, and the homodimer binding sites Arg97 and Tyr101 are important for HSD17B13 enzymatic activity. A: Ribbon diagram for the predicted structure of the substrate binding sites of HSD17B13 with retinol as the substrate. Retinol and essential residues are labeled and shown as sticks. B–E: Enzymatic activity of mutant HSD17B13. HEK293 cells were seeded 1 day before and transiently transfected in triplicate with HSD17B13, HSD17B13 mutant, or empty vector plasmids. All-trans-retinol was added to the culture and incubated for 6 or 8 h. Retinaldehyde and retinoic acid were separated by normal-phase HPLC and quantified by retinoid standards. Retinoid levels were normalized to protein concentrations and are shown as relative value to empty vector controls. Data are presented as mean ± SEMs. WT, wild-type (variant A).