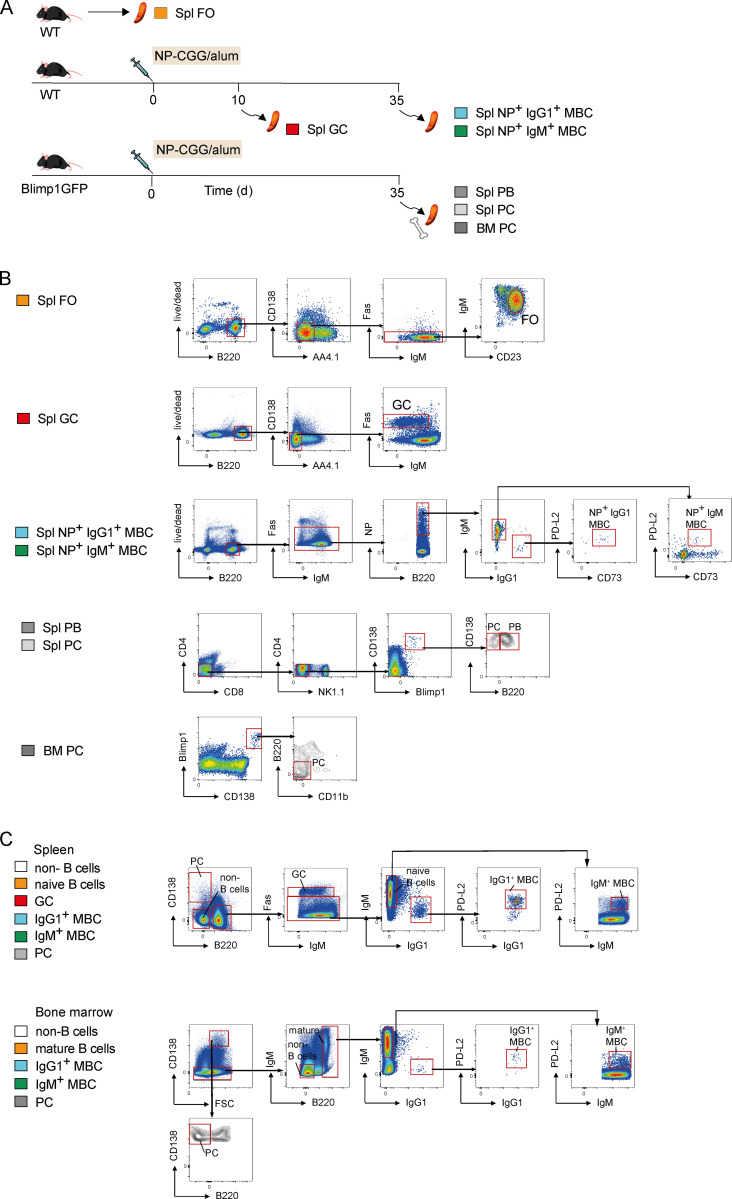
Figure S3.
Flow cytometric gating strategy for B cell populations sorted for RNAseq analysis and for analysis of BAFFR and TACI expression. (A) Spleens were harvested from WT mice or from WT or Blimp1GFP mice that were immunized with NP-CGG in alum on day 0, followed by dissection of spleen or bone marrow on days 10 and 35. (B) FO B cells (Spl FO, B220+CD138−AA4.1−Fas−IgMloCD23+) from spleens of unimmunized WT mice, GC B cells (Spl GC; B220+CD138−AA4.1−Fas+) from WT spleens 10 d after immunization with NP-CGG in alum, NP+ IgM+ MBCs (Spl NP+ IgM+ MBC; B220+Fas−NP+CD73+PD-L2+IgM+IgG1−), and IgG1+ MBCs (Spl NP+ IgG1+ MBC; B220+Fas−NP+CD73+PD-L2+IgM−IgG1+) from WT spleens 35 d after immunization with NP-CGG in alum and splenic PBs (Spl PB, CD4−CD8−NK1.1−CD138hiBlimp1hiB220+), splenic PCs (Spl PC, CD4−CD8−NK1.1−CD138hiBlimp1hiB220−), and bone marrow PCs (BM PC, CD138hiBlimp1hiB220−CD11b−) from Blimp1GFP mice 35 d after immunization with NP-CGG in alum were flow sorted and analyzed by RNAseq. Three to five mice were pooled to obtain the required cell numbers for each biological replicate of each population. Red boxes indicate gates used to isolate subsets of cells. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of splenocytes and bone marrow from WT mice immunized with NP-CGG in alum as described in A for the analysis of BAFFR and TACI expression shown in Fig. 3, B and C, showing gating strategy for total splenic (B220−CD138−) and bone marrow (B220−CD138−IgM−) non–B cells, splenic (PC; B220−CD138hi) and bone marrow PCs (FCShiB220−CD138hi), splenic GC B cells (GC; CD138−B220+Fas+), splenic naive B cells (B220+CD138−Fas−IgM+), bone marrow mature B cells (B220hiCD138−), splenic IgM+ and IgG1+ MBCs (B220+CD138−Fas−PD-L2+), and bone marrow IgM+ and IgG1+ MBCs (B220hiCD138−PD-L2+). Red boxes indicate gates used to isolate subsets of cells.